

Switzerland will spoil you with a fantastic transport system - swift and disturbingly punctual trains, clean buses, and half a dozen different kinds of mountain transport systems, all integrated into a coherent system. The discount options and variety of tickets can be bewildering, from Half Fare Cards to multi-day, multi-use tickets good for buses, boats, trains, and even bike rentals. In general, there's at least one train or bus per hour on every route. On many routes there are trains and buses running every 30 or even 15 minutes, with city transit services running every 5-7 minutes during rush hours. However, as with everything in Switzerland the transit runs less often, or at least for a shorter period of the day during weekends, and particularly on Sundays and public holidays and in less densely inhabited areas.
Information, routes, fares, policies and schedules for almost all public transport can be found online on the Swiss Federal Railways' (SBB CFF FFS) website which is a must-use resource for any traveller to Switzerland. Information can also been found on posters and screens at any stop, or from a ticket window at any railway station. The nation-wide coherently integrated timetable is also available as a free smart phone app[dead link]. At any railway station of any provider you can get information and tickets (at manned ticket counters) for any of the many members of the integrated railways network of Switzerland and most bus systems, in particular PostBus Switzerland (de: PostAuto, fr: CarPostale, it: AutoPostale) which provides an online timetable as well with the same data.
Bus and trains do not and are not allowed under law to compete each other in Switzerland, rather - quite the opposite, they are complementary to each other – besides being coordinated timetable-wise. That way, almost all inhabited villages and towns in Switzerland can be reached by public transport. This is actually constitutionally demanded by the Public Service regulations of the Swiss Confederation. Public Service is a unique Swiss term loosely referring to all kinds of laws, acts, and ordinances, which define the basic supply of public services and infrastructure in particular concerning postal services, telecommunication, electronic media, public transport and road infrastructure.
There are about 20 regional fare networks throughout the country, which incorporate many kinds of public transport (city bus, tram, metro, any kind of train, PostBus, boats, funiculars and others) by many different providers around urban centers into one single fare system, such as ZVV in the canton of Zurich, unireso (see also: Geneva's tpg) in the canton of Geneva and its French adjacent area, or mobilis around Lausanne in the canton of Vaud at the northern shore of Lake Geneva, passepartout in the cantons of Lucerne, Nid- and Obwalden (keyword: Titlis). Usually these networks sell zone-based tickets valid for a particular time frame (instead of point-to-point tickets) for journeys within their fare network borders. Many of these networks and transit operators provide their own free smartphone apps; sometimes to be found on the major city's transit company website.
Even if there is no train or city transit available, the comprehensive PostBus Switzerland network gets you there. Where applicable, PostBus Switzerland is part of regional fare networks. You find all timetable information on Swiss Federal Railways' (SBB CFF FFS) online timetable, but PostBus Switzerland also provides their own free app with the same information as by SBB as well as many additional features.
Further information about the railway network in Switzerland[dead link] and the Switzerland-wide countryside bus network[dead link] is also available online.
Tickets
[edit]
Public transport fares in Switzerland are usually set for two or more years and can easily stay fixed for ten years. This isn't surprising as changes in fares are easily a widely discussed political issue and regularly subject to public vote. If the fares do change, then only during the timetable change in December, otherwise the prices are stable.
Therefore, Swiss usually buy their ticket just a few minutes before departure, if they don't own a travel card or did not buy it online just for the sake of convenience. This is also a reason why you can buy domestic tickets at the earliest only 2 months before the date of travel.
There is however one exception: The supersaver tickets, which are only sold online, are only valid for a particular connection and only available online no more than 60 days before travel date.
Ticket validity
[edit]A standard domestic train ticket is usually valid for the entire calendar day until the end of day service (which is 05:00 of the next day), but just for one journey of the selected route. And normally, you are allowed to make intermediate stops and continue later on the same day.
Exceptions are supersaver tickets sold by the SBB CFF FFS, which are only valid for a particular connection.
Often, tickets are sold for a route which includes different providers and/or different kind of transport means. If the start and final destination are not in the same fare network, the previously mentioned validity is applicable.
Tickets sold for routes within fare network borders are often zones-based instead of point-to-point tickets and therefore only valid for any route which stays inside the indicated zones. They are valid for a particular time frame and usually valid for any number of journeys within this frame time (e.g. 1/2 hour, 1 hour, 2 hours for "one-way" tickets, or the whole calendar day, or even for 24 hours). These conditions can differ from fare network to fare network, though they are often very comparable or sometimes even the same, but check them beforehand.

Generally, standard domestic train tickets are always valid for any type of train, even for tourist trains (but it's possible you must also have a reservation for them) and for international trains as long as these trains take the same route as indicated on your ticket and you travel only between Swiss train stations (including some stops outside of Switzerland[dead link]).
International tickets for international connections traversing the Swiss border usually have a quite different validity and are also often restricted to particular trains and/or type of trains. But on the Swiss travel system, they usually have at least the same validity as domestic tickets and are often valid even for more than one day. But make sure to check their particular conditions carefully!
Deductions
[edit]Almost nobody in Switzerland pays full fare for the transit system. At the very least they all have a Half-Fare Card (fr: abonnement demi-tarif, de: Halbtax-Abonnement, it: abbonamento metà-prezzo) which saves you 50% on all national buses and trains and gives a discount on local and private transit systems. Press the '1/2' (or tarif reduit, reduzierter Preis, tariffa ridotto) button on the ticket machines to indicate you have this card, and be prepared to hand it to the conductor along with your ticket on the train. Annual half fare cards cost Fr. 185 for adults (over 25 years old) and Fr. 120 (between 16 and 25 years old); visitors from abroad[dead link] can buy a 1-month Swiss Half-Fare Card for Fr. 120.
You save Fr. 65 on a round-trip ticket from Zurich to Lugano, so if you are planning on travelling a lot, the card will quickly pay for itself. Children between the ages of 6 and 16 pay half price for travel around Switzerland. Children travelling with their parents have the option to acquire a yearly card for Fr. 30 called Junior Travelcard, subsequently travelling for free as long as accompanied by one of the parents. A similar option is available for the same price when accompanied by a single person over 16, called the Children’s Co-Travelcard (the card is personal both for the child and accompanying person). Parents from abroad in possession of any kind of a valid Swiss Travel Pass/Card/Ticket from the Swiss Travel System can get a Swiss Family Card for free with the same advantages.
Travel cards
[edit]The most convenient way to travel with public transport in Switzerland is with a GA travel card (de: Generalabonnement, fr: abonnement général, it: abboamento generale), or for visitors only a Swiss Travel Pass (equally valid like a GA travel card). The GA card grants you access to all national buses, including PostBus Switzerland, and railways, many boats, all city transit systems, and offers travellers a hefty discount on many privately operated cable cars, funiculars, and some ski lifts. Swiss Travel Passes range in price from Fr. 232 for a 3-day, 2nd class pass to Fr. 675 for a 15-day pass, 1st class. There is also a Swiss Travel Pass Flex, which is slightly more expensive but can be used over non-consecutive days within a month. Like the Half-Fare Card, you can buy these passes from any railway station ticket office or simply online.
There are a few other possibilities in between a Half-Fare Card and a Swiss Travel Pass: See an overview here.
Reservation and "Tourist trains"
[edit]In general, you will always find a free seat on a train, except during rush hours (departure times ca. 06:30-08:00, and about 17:00-18:30); free seats may be hard to find on non-stop connections between the major business cities and its suburbs. In particular between Zurich and Bern, between Zurich and Basel, and between Lausanne and Geneva in both directions. You can easily check this on the online timetable by the statistically based occupancy indication updated daily and available from 30 days before departure.
Normally, you do not need a reservation for any of the public transport system in Switzerland. Often, a reservation is not even possible, in particular for local trains. Though, there are some exceptions. Besides the scenic trains mentioned below, some of the yellow bright PostBus lines require reservation[dead link] as well. The easiest way to check this is by using the online timetable. If you find a capital R on the timetable indicated next to a particular connection, then a reservation is possible. If you find a capital R in a square, then a seat reservation is compulsory. And of course, a reservation is compulsory (and automatically bundled in the tickets) for many of the international connections, particularly for TGVs to/from France, and ECs to/from Italy.
Only two trains within Switzerland require reservations: the Bernina Express (BEX), running daily between Chur / Davos and Tirano and the Glacier Express (GEX) running between St. Moritz / Davos and Zermatt. However, it is also possible to travel the same routes using regular (regional) trains. These trains stop often and you have to change trains two or three times for the whole route, but the train connections are well coordinated.
Reservations is also recommended during high seasons for the GoldenPass Line between Montreux and Interlaken, as well as for the Gotthard Panorama Express[dead link] between Luzern and Flüelen by boat and also for further travel between Flüelen and Lugano/Locarno in the southern Ticino through the 15 km long St. Gotthard summit Tunnel in the middle of the Alps by train; and its several spiral tunnels instead through the world's longest railway tunnel, the Gotthard Base Tunnel of 57.1 km, where you will hardly perceive that you are traversing the largest and highest mountain range in western Europe, the Alps.

Since the opening of the Gotthard Base Tunnel in 2016, however, the transfer between Italy/Southern Switzerland (Milano, Lugano, Locarno, Bellinzona) and Northern Switzerland (Luzern, Zurich, Basel) has become often very occupied due to the even easier and faster connection. During tourists' rush hours; trains running through the Gotthard Base Tunnel can get totally occupied, and travellers without a reservation will be prevented from entering fully booked trains, since the SBB does not allow standing passengers on trains through the world's longest railway tunnel (takes 20 minutes for traversing, one hour between Bellinzona and Arth-Goldau). So make sure to check the occupancy on this route and to make a reservation, if necessary.
For the Pre-Alpine Express (VAE)[dead link] between Luzern and St. Gallen/Lake Constance in north-eastern Switzerland you do not need any reservation. For the Lötschberger between Bern, Spiez in the Bernese highlands and Brig in the Valais over the old, 500-m-higher line and 14-km-long Lötschberg summit Tunnel you also don't need a reservation.
During winter season on weekends to and from major ski areas, trains can be packed.
Buy the tickets before you board
[edit]On many trains in Switzerland, tickets can no longer be bought on board, so it is highly advised to buy tickets beforehand. You will get heavily fined if you don't have a ticket.
The red-grey ticket machines accept credit/debit cards. You can also buy a ticket, either, at any manned ticket counter, or online on the Swiss Federal Railway (SBB CFF FFS) website and can be displayed on your laptop, tablet or smartphone – even without the app, or on SBB's smart phone app[dead link], if you have an account registered with a valid payment method (credit/debit card, invoice, Postfinance, Reka or Twint). But take care – they must be bought before the train leaves the station (automatic time checks with timetable by the scanners) and you are responsible for the working condition of your smart phone (so make sure you have enough battery.)
One exception is PostBus Switzerland, where you still can purchase your ticket with the driver on board; for most routes to any destination in Switzerland. PostBus Switzerland provides now the same mobile ticketing service with their own PostBus App.
Travel
[edit]
Schedules
[edit]Using trains is easy, although the number of different kinds of trains can be a bit confusing unless you know that the schedules at a Swiss railway station are colour-coded. The yellow sheet is for departures (fr: Départ, de: Abfahrt, it: Partenza) and the white sheet is for arrivals (fr: Arrivée, de: Ankunft, it: Arrivo). Faster express trains appear on both of these sheets in red, while the trains in black stop at more stations.
For trips with transfers it is often easier to use online timetable information, as it will pick transfers for you. You need not fear transfers of five minutes or less. You will make them, provided you are ready to de-board at the exit before the train stops, and provided you know which platform you arrive on and which one you depart from. The online app, information screens, and speaker announcements will help you to prepare accordingly. Many Swiss commute with a one or two minute transfer between trains, providing the distance between the tracks allow it.
On departure and arrival posters you can consult the standard platform, indicated by a track number. Departure/Arrival screens and boards, as well as SBB's online timetable and smart phone app provide you with eventually updated information. Online you can also track the current location of a train, as well as other real-time information.

Train composition
[edit]At the track, overhead displays indicate the (larger and) final destination(s) and the official departure time. The small numbers and letters along the bottom show you where you can board the train. The letters indicate the platform area you should stand in, so called sectors of the platform indicated by blue overhead signs with large capitals (such as A, B, C, D, E, or F), and the numbers indicate the class. The class (1st or 2nd) is indicated by a "1" (and a thick, horizontal yellow stripe on the coach's outside) or "2" on the side of the coach, these correspond with the numbers on the overhead display. This train composition information (class number, bicycle coach, family coach, restaurant/bistro coach and respective sector letter) you can also find online for most domestic trains (as of 2019 the ones operated by SBB or BLS) and international trains leaving from or arriving in Switzerland (with exception of TGV) of a particular connection with a departure or arrival time quite close to the future (online timetable: by clicking the plus sign next to platform number; SBB Mobile app: by selecting the respective stop name in the details). In addition most bigger stations will have a printed plan (blue sheet) with the train compositions of most major trains on the platform.
All Swiss trains are non-smoking — this is also indicated on the side of coach, as well as inside.

Luggage
[edit]Small luggage, coats and jackets can be stowed above your seat. In most trains where four seats build a compartment you can store small and middle sized luggage between the backs (!) of the seats. For larger luggage you often find a rack at the end of the coach. During busy periods, people often stow large luggage (or skis) in the entrance area in between coaches. This is usually fairly safe, but apply common sense and keep an eye on them. Further, SBB provides a totally safe and effective nation-wide luggage delivery service[dead link] to any manned railway station, or Post office reachable by PostBus (usually called "<village name> Post/Posta") destination, especially addressed to tourists and skiers with large, heavy luggage or many suitcases, or even door-to-door, so that you can fully enjoy you journey and make your swift transfers easily and without any hassle.
Types of trains
[edit]
The many different types of trains is bewildering at first, but is actually quite simple.
The routes the SBB timetable suggests will make much more sense if you understand them. All trains have a one or two letter prefix followed by a line number (new since 2017/18) and a train number.
For example IC 2 889 for the InterCity between Zurich HB and Lugano (no. 2) leaving Zurich at 17:32, or S 3 12323 for the mobilis S-Bahn line no. 3 (suburbain train) leaving at 07:52 from Villeneuve to Allaman and also connecting Montreux with Lausanne.
Only the prefix, the line number (if available), the destination, and the time of departure are important. Sometimes, for regional lines, there is no line number given as for example in RE 3823 for the RegionalExpress train leaving at 12:50 from Bulle to Berne.
However, your regular ticket will be valid for all of them including tourist and international trains for domestic journeys, given they run the same route within the Swiss travel system. Normally, a train ticket is valid the entire calendar day until the end of day service (05:00 of the next day), but just for one journey. And, normally, you are allowed to make intermediate stops and continue later on the same day. Exceptions are SBB's supersaver tickets, which are only valid for a particular train connection, and fare network tickets (check their own regulations.)
- Local, "slow" trains:
- R (Regio/Régional) trains are local trains. They stop everywhere or almost everywhere, and generally reach into the hinterlands of a major station like Lausanne, but not to the next major station (in this case Geneva). If you are going to a small town, you may transfer at a larger station to an R train for the last leg.
- Suburban trains are usually indicated by an S (for S-Bahn) and followed by the number of the line, such as S 12.
- RE (RegioExpress) trains generally reach from one major station to the next, touching every town of any importance on the way, but don't stop at every wooden platform beside the tracks.
- Fast trains:
- IR (InterRegio) trains are the workhorses of Swiss transit. They reach across two or three cantons, for instance from Geneva, along Lake Geneva through Vaud, and all the way to Brig at the far end of the Valais. They only stop at fairly large towns, or railway junctions.
- IC (InterCity) trains are express trains with restaurant cars. They are sumptuous and comfortable, often putting vaunted services like the TGV to shame, and make runs between major stations, with occasionally stops at a more minor one where tracks diverge.
- Former ICN trains (InterCityNeigezug, or Intercity Tilting Train) are now branded as IC trains, as well. They are the express tilt-trains, as luxurious as the IC trains. They run between major cities like Geneva, Lausanne, Biel/Bienne, Zurich, Brig, Lugano, Luzern and Basel.
There are also a number of narrow gauge railways that don't fit this classification that supplement the buses in the hinterlands, such as the line from Nyon to La Cure or the line from Interlaken to Lauterbrunnen.
All trains are integrated into regional fare networks, if existing. Therefore you can use zone-based tickets on them, but, of course, only for journeys within the borders of the fare network, so take care about the validity of your ticket. This is especially taken into consideration for journeys with local train systems, such as on R and S trains. Often, ICs and ICNs do not stop a second time within the fare network, so tickets by the regional fare network would be of no use on them.
Bicycle
[edit]You can bring your bicycle on almost every train in Switzerland (check the timetable, sometimes you must make a reservation, or it is not allowed at all, e.g. on international connections), with two provisos: you must have a ticket for it (either a regular ticket, a half-fare ticket if in possess of a valid Half-Fare Card, or a day pass for Fr. 14), and you must get on at a door marked with a bicycle. On ICN trains and some IR trains this is at the very front of the train.
Dogs
[edit]You are allowed to bring your dog onto the train, however you have to purchase an extra ticket for the dog. Independent of the class of travel, you have to buy a second class half-fare ticket or the stipulated minimum fare. For bigger trips it might be worthwhile to buy a day card for your dog at Fr. 25. An exception to this are dogs below 30 cm shoulder blade height, which can travel for free as hand luggage provided they are in a carrier or basket. More information on travelling with dogs can be found on the SBB CFF FFS website.
International connections
[edit]Switzerland is, together with Germany, one of the most centrally located countries in Europe, and trains arrive from all parts of Europe. Some major routes include:


- The TGV Lyria (Train à grande vitesse, French/Swiss high-speed railway connection), with several trains daily from/to Paris, Dijon, Lyon, Avignon, Aix-en-Provence and Marseille.
- Examples of travel time: Paris-Geneva 3 hr, -Lausanne 3½ hr, -Basel 3 hr, -Berne 4 hr, -Zurich 4 hr;
- and Geneva-Lyon 2 hr, -Avignon 3 hr, -Marseille 3½ hr;
- Examples of travel time: Milano-Berne 3 hr, -Basel 4 hr, -Geneva 4 hr, and Milano-Zurich 3½ hr (about 5 hr, if you choose the route over the Gotthard line (opened in 1882) via Göschenen and Airolo instead through the world's longest railway tunnel, the 57-km-long Gotthard Base Tunnel)
- Regular ICE (InterCity Express, German high-speed trains) from Zurich and Interlaken via Berne, Basel to Freiburg i.B., Offenburg, Baden-Baden, Karlsruhe, Mannheim, Frankfurt a.M. (main railway station or airport) in Germany, many continuing toward Cologne and Dortmund, or Hannover and Hamburg, or Berlin, or Amsterdam.
- Examples of travel time: Frankfurt Airport-Basel 3 hr, -Berne 4 hr, -Interlaken 5 hr, -Zurich 4 hr
- Regular IC (InterCity) trains between Zurich and Stuttgart, travel time 3 hr
- Regular EC (EuroCity) trains between Zurich and Munich, travel time 4 hr
- Regular RJ (RailJet) trains between Zurich and Innsbruck (3½ hr), Salzburg (5½ hr), Vienna (8 hr) in Austria, and further to the east
- Sleeper trains operated by ÖBB as Nightjet
You can use most of these trains with the exception of night trains domestically in Switzerland with a normal domestic ticket, but keep in mind that they may arrive at the end of a long journey and may not reach the very high Swiss standards for punctuality.
Information for railway enthusiasts
[edit]
In Switzerland, more than 99% of the railway infrastructure is electrified, but it is possible to find steam railways such as the Brienz Rothorn Railway, the Furka Cogwheel Steam Railway and others.
There are many interesting mountain railways of all types. In Switzerland most electric trains get their power from a single phase AC network at 15,000V 16 2/3Hz. This network uses its own power lines run with 66 kV and 132 kV, which have, unlike normal power lines, a number of conductors not divisible by 3. Most power lines for the single phase AC grid of the traction power grid have four conductors. Railway photography is permitted everywhere provided you don't enter forbidden areas without permission.
Here is short list of the most remarkable railway lines:
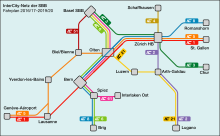
- The Glacier Express (GEX) between Davos / St. Moritz (en: Grisons, de: Graubünden) and Zermatt (Valais), an 8-hour trip through the central Swiss Alps. The train has special wagons with curved windows on the roof, supplement required. Views in all directions .
- The Bernina Express (BEX) between Davos / Chur and Tirano in Italy, via Pontresina / St. Moritz over the Bernina pass (2253m o.s.l.) the highest rail transversal in the Alps, high mountain scenery. The train has special wagons with curved windows on the roof with views in all directions. Supplement required.
- The Pre-Alpine Express (VAE, Voralpenexpress) running between St. Gallen / Lake Constance and Lucerne, through the rolling hills of the Appenzellerland down to Rapperswil, where it crosses the first, eastern part of Lake Zurich, then up again through the lovely moor of Rothenturm (saved from military destruction by a publicly initiated referendum in 1987) and close to Einsiedeln down again to Arth-Goldau at the bottom of the Rigi and further to Lucerne along the Lakes of Zug and Lucerne.
- The Jungfrau Railway, from Interlaken (560 meters) to the Jungfraujoch station (3450m a.s.l.) in two hours. Definitely the most impressive journey in the Alps.
- The Gornergrat Railway, departure from Zermatt to the 3090m a.s.l. high Gornergrat.
- The Mount Rigi Railway, oldest mountain railway in Europe.
- The Mount Pilatus Railway, from Lucerne to the top, the steepest (max. 48% gradient) railway in the world.
- The Brienz Rothorn steam cogwheel railway above lake Brienz to the Rothorn summit (2350m a.s.l.) and almost exclusively run by steam locomotives.
- The Lötschberger is a line connecting Berne / Spiez (Bernese Highlands) and Brig (Valais), not considered as a mountain train but with still impressive scenery, especially if you take the route by a regional train ('RE') through the old 14.6-km-long Lötschberg summit tunnel (between Kandersteg and Goppenstein, 500 m above the 34.6-km-long Lötschberg Base Tunnel, a high-speed train tunnel opened in 2007).
- The St. Gotthard line[dead link] with its many spiral train tunnels and the 15-km-long St. Gotthard summit train tunnel (built between 1872 and 1882, 199 workers lost their lives in its construction) connecting the German spoken northern Switzerland Zurich/Luzern and the Italian spoken southern Switzerland Ticino (Bellinzona, Lugano, Locarno). Also advertised as the Gotthard Panorama Express[dead link] between Luzern and Flüelen by boat, and further then by train to either Bellinzona, or Locarno/Lugano.

