| Note: There is a moderate level of civil unrest, crime and terrorist activity in some parts the country, but in particular Jammu and Kashmir, near the India-Pakistan border where most governments advice have a "Do not travel" warning. There are also a few extremist groups in the North-Eastern parts of the country, such as in the states of Assam and Manipur. | |
Travel advisories
| |
| (Information last updated 30 May 2021) |
| COVID-19 information: Travellers arriving in India must submit a self-declaration form at the Air Suvidha portal. A negative RT-PCR test report issued 72 hours before the time of travel will be required. Alternatively, travellers vaccinated with a WHO recognised COVID-19 vaccine can upload their vaccination certificate and are not bound to undergo RT-PCR testing. Exceptions may apply. Lockdowns and curfews may apply in some states. See the advisory issued by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare for details. For the latest information, please check the National Health Ministry Portal and Directorate General of Civil Aviation Portal. | |
| (Information last updated 12 Feb 2022) |
India (Hindi: भारत or Bhārat), the largest country in South Asia, has many of the world's highest mountains, most populated cities, and longest rivers. India's heritage and culture is a rich amalgam of the past and present. This vast country, the second most populous in the world and set to become number one, offers the traveller a view of fascinating religions and ethnography, a smorgasbord of languages, and architectural masterpieces that were built millennia ago and remain intact today. As the nation opens up to a globalised world, India still has a depth of history and intensity of culture that awe and fascinate the many who visit there.
Regions
India is administratively divided into 28 states and 8 union territories. The states are broadly demarcated on linguistic lines. They vary in size; the larger ones are bigger and more diverse than some countries of Europe. The union territories are usually much smaller than the states—sometimes they are just one city—and they have much less autonomy. India has two island chains off the mainland – the Andaman and Nicobar Islands in the Bay of Bengal and the Lakshadweep in the Arabian Sea.
The states and union territories are grouped by convention into the following regions:
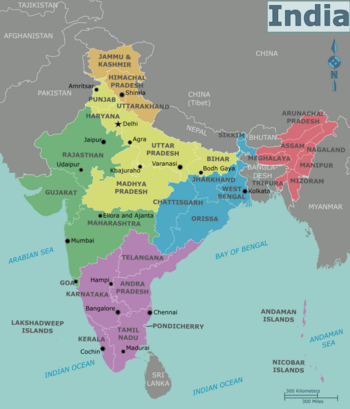
| Himalayan North (Jammu and Kashmir, Ladakh, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand) Mountainous and beautiful, a tourist destination for the adventurous and the spiritual. This region contains some of India's most visited hill stations and religious places. |
| The Plains (Bihar, Chandigarh, Delhi, Haryana, Madhya Pradesh, Punjab, Uttar Pradesh) The plains, India's breadbasket, are watered by the holy rivers Ganges and Yamuna and their tributaries. The region also features the country's capital, Delhi, Agra of Taj Mahal fame and the holy cities of Allahabad, Mathura, Varanasi and Bodh Gaya. Many of the events that shaped India's history took place in this region. |
| Western India (Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu, Goa, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Rajasthan) Home to the vast Thar Desert; the colourful palaces, forts and cities of Rajasthan; the country's most vibrant and biggest city, Mumbai; the mesmerising rock-cut caves of Ajanta and Ellora in Maharashtra; pristine forests; the wonderful beaches of Goa; the Asiatic lions of Gujarat in Gir jungles; and the rapidly developing cities of Ahmedabad, Surat, Jaipur and Pune. |
| Southern India (Andaman and Nicobar, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Lakshadweep, Pondicherry, Tamil Nadu, Telangana) Features famous and historical temples, tropical forests, backwaters, beaches, hill stations, and the vibrant cities of Bangalore, Chennai, Thiruvananthapuram and Hyderabad. The city of Mysore is world-renowned for its palaces, especially the Mysore Palace. The island groups of Andaman and Nicobar (on the east) and Lakshadweep on the west, included in this region for convenience, are far from the mainland and have their own unique characteristics. |
| Eastern India (Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Odisha, Sikkim, West Bengal) Economically less developed, but culturally rich and perhaps the most welcoming to outsiders. Features Kolkata, once the capital of British India, and the temple cities of Puri, Bhubaneswar and Konark. The region stretches from the mountains to the coast, resulting in fascinating variations in climate. It is also the mineral storehouse of India, having the country's largest and richest mines. |
| North-Eastern India (Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Tripura) Insular and relatively virgin, this is the country's tribal corner, with lush, beautiful landscapes, endemic flora and fauna of the Indo-Malayan group and famed tea gardens. Consists of seven states popularly known as the "Seven Sisters". The world's oldest pologround, world's only floating national park, world's only women run market, world's tallest topiary plant and world's only floating lake can be seen in Manipur. The state of Meghalaya is depicted as the "Scotland of India" because of its mesmerizing environment. World's tallest railway bridge is also under construction in Manipur. |
Cities
These are nine of India's most notable cities. Other cities can be found under their specific regions.
- 1 Delhi — the capital of India and the heart of Northern India
- 2 Bangalore (Bengaluru) — the beautiful garden city, once the sleepy home of pension takers, now transformed into an IT hub for high-technology companies and sprouting pubs.
- 3 Chennai (Madras) — the main port in Southern India, cultural centre, automobile capital of India
- 4 Hyderabad — known for pearl and diamond trading, now with major manufacturing and financial institutions
- 5 Jaipur — the Pink City, a major exhibit of the Hindu Rajput culture of medieval Northern India
- 6 Kochi (Cochin) — the Queen of the Arabian Sea, historically a centre of international trade, now the gateway to the sandy beaches and backwaters
- 7 Kolkata (Calcutta) — the cultural capital of India, known as the City of Joy, and home to numerous colonial buildings
- 8 Mumbai (Bombay) — the largest city and the financial capital of India, the city that never sleeps, home of "Bollywood", the Hindi film industry
- 9 Varanasi (Banaras or Kashi) — considered the most sacred Hindu city, on the banks of the Ganges, one of the oldest continually inhabited cities in the world
Other destinations
India has many outstanding landmarks and areas of outstanding beauty. Here are some of the most notable.
- 1 Bodh Gaya — the main temple complex, which includes the Mahabodhi temple, is the place where the Buddha Sakyamuni attained enlightenment
- 2 Ellora and 3 Ajanta — spectacular rock-cut cave monasteries and temples, holy place for the Buddhists, Jains and Hindus
- 4 Golden Temple — Sikh holy site in Amritsar
- 5 Hampi — the awesome ruins of the empire of Vijayanagara
- 6 Khajuraho — temple complexes famed for their erotic sculptures
- 7 Konark — Sun Temple, a unique example of Kalingan architecture, which is a UNESCO World Heritage site
- 8 Meenakshi Temple — a spectacular Hindu temple in Madurai
- 9 Taj Mahal — the incomparable marble tomb in Agra, one of the Seven Wonders of the Modern World
See also:
- Forts and palaces of India
- Indian national parks and wildlife sanctuaries
- Indian zoos and botanical gardens
- Natural wonders of India
- Sacred sites of the Indian subcontinent
- Hill stations in India
- UNESCO World Heritage List (India)
Understand
One thing that foreign visitors need to know is that India is, in many ways, heterogeneous. If they experience one set of behaviours from the locals in one part of the country, it does not mean that the same behaviour is common in another area. To give a very simple example, a taxi driver in Mumbai will without saying a word drop their meter flag and return the exact change, while in Delhi you have to tell the driver to use the meter and hope you get your change, and in other areas taxi drivers don't even have meters and have fixed the rates for even short distances, and you just pay the amount demanded; if you do get an honest driver, consider yourself lucky. India shows extreme variation in most things, and one needs patience and luck to find the best. Never assume you know everything about any aspect of India; be prepared to see completely new things every day.
History
- See also: Mughal Empire, British Raj

Humans are thought to have first migrated into the Indian subcontinent around 70,000 BCE and there are some archaeological sites for stone age India. One important one is at Mehrgarh (Pakistan), with the oldest known evidence of agriculture in the subcontinent, around 7000 BCE.
The Indus Valley Civilization (3300-1300 BCE) was one of the world's first Bronze Age civilizations and very advanced for its time. At its peak (2600-1900 BCE) it covered most of what is now Pakistan, plus some of northern India and eastern Afghanistan. The two biggest archaeological sites, both in Pakistan, are Mohenjo-daro and Harappa.
Some time after 2000 BCE, the Aryans, herdsmen from somewhere to the northwest, migrated into the region. At about the same time, related groups invaded Greece (Hellenic Greeks displacing Minoans), Anatolia or Turkey (the Hittites), Persia and other areas. It is believed that all these tribes spoke related languages and many modern languages, including most of those spoken in northern India, Europe and some in Central Asia, are descended from them. Linguists classify them all in the Indo-European language family.
The Vedic Period is dated to roughly 1500-500 BCE. This was the period when the Vedas, the oldest and holiest books of Hinduism, were compiled. They were in an Indo-Aryan language, Vedic Sanskrit. Although few details and archaeological findings are available for this period, many rituals of Hinduism took shape during that period.
The Vedic civilisation influences India to this day through the dharmic religions. Present-day Hinduism traces its roots to the Vedas, but is also heavily influenced by literature that came afterward, ranging from the Upanishads and Puranas, to the great epics — Ramayana and Mahabharata. By tradition, these texts are claimed to only expand and distill the knowledge that is already present in the Vedas.
A section of the Mahabharata called the Bhagavad Gita is among the most widely read works. The Gita is said to be a concise summary of the four Vedas of Hinduism. Kaal (Kshar Brahm) is said to have described the knowledge of Gita in 700 verses of 18 chapters after entering in Shri Krishna's body. It is a dialogue, just before a great battle at Kurukshetra, between the hero Arjuna and the God Krishna who serves as his charioteer. Today Kurukshetra is a destination for both pilgrimage and tourism.
In the 1st millennium BCE, various schools of philosophical thought developed, enriching Hinduism greatly. Most of them claimed to derive from the Vedas. However, some of these schools, two of which were Buddhism and Jainism, questioned the authority of the Vedas, and they are now recognised as separate religions.
Many great empires arose between 500 BCE and 590 CE. Notable among them were the Mauryas and the Guptas, both with their capital in the city of Pataliputra, now called Patna. The Gupta Empire (3rd century CE to 590 CE) is often called the Golden Age of India. Further west, the Gandharan civilisation (an independent kingdom, later part of the Maurya Empire) ruled much of what are now Pakistan and Afghanistan. Their city Taxila was a great centre of Buddhist and other learning.
Over time there was a gradual decline of Buddhism and Jainism. The practice of Buddhism, in particular, disappeared from India's heartland, though Buddha himself was incorporated into the Hindu pantheon. Jainism continues to be practised by a significant minority who are ambivalent about whether they consider themselves Hindus or not. Hinduism itself went through major changes. Vedic deities such as Indra and Agni became less important while Puranic deities such as Vishnu, Shiva, their various Avatars and family members gained prominence.

Islamic incursions started in the 8th century. Gradually the raiders started staying as rulers, and soon much of North India was ruled by Muslims. The most important Muslim rulers were the Mughal Empire that at its peak covered almost the entire subcontinent (save the southern and northeastern extremities), while the major Hindu force that survived in the North were the Rajputs. The bravery of the Rajputs in resisting invasion of their land is legendary and celebrated in ballads all over the forts of Rajasthan. Prominent among the Rajputs was Maha Rana Pratap, the ruler of Chittorgarh, who spent years in exile fighting Akbar, the third of the Mughals. Eventually, however, the Rajputs were subdued. Some Mughal armies had a high proportion of Rajput officers, although some Rajput rebellions still occurred during the reign of Jahangir, Shah Jahan and Aurangzeb. This period of North India produced the monumental gems of Rajasthan and the Taj Mahal. Hindi and Urdu also took root in medieval North India. During the Islamic period, there were Hindus that converted to Islam, often forcibly, or to avoid the Jizya tax, as told by Muslim chroniclers. Today, around 15% of India's population follow Islam.
Sikhism, another major religion, was established in Punjab during the Mughal period. Relations between Sikhism and the Mughals varied over time. The Golden Temple at Amritsar was built and recognised all over the world as Sikhism's major pilgrimage centre. By the time of its tenth Guru however, Guru Gobind Singh, relations were hostile, primarily due to the antagonism of Aurangzeb, the most intolerant, brutal and bigoted of the Mughals. Conflict between the Sikhs and the Mughals was one of the causes for the eventual decline of the Mughal Empire. Another reason was the rise of the Maratha Empire in Maharashtra, which was started by Shivaji and carried on by the Peshwas. The Marathas established a short-lived confederacy that was almost as large as the Mughal Empire. Marathas lost their command over India after the third battle of Panipat, which in turn paved a way for British colonialism.

South India followed a different trajectory, being less affected by Islamic rule. The period from 500 to 1600 CE is called the classical period and was dominated by great South Indian kingdoms. The most prominent empires included the Chalukyas, Rashtrakutas and Vijayanagara who ruled from present day Karnataka and the Pallavas, Cheras, Pandyas and Cholas who ruled from present day Tamil Nadu and Kerala. Among them, the Cholas, who ruled from various capital cities including Thanjavur and Gangaikondacholapuram, are widely recognised to be the most powerful of the South Indian kingdoms, with their territory stretching as far north as Pataliputra and their influence spreading as far east as Sumatra, western Borneo and southern Vietnam at the height of their power. Some of the grandest Hindu and Jain monuments that exist in India were built during this time in South and East India.
Northeast India was also fairly isolated from the rest of the country until the colonial period. The largest and longest kingdom to rule over the Northeast were the Ningthouja dynasty (33 AD - 1891 AD) of Manipur, followed by the Ahoms who, from the 13th to 19th centuries, successfully defended Assam and neighbouring regions from Mughal expansion.
European traders started visiting India beginning in the late 16th century. Prominent among these were the British, Dutch, French and the Portuguese. The British East India Company made Calcutta their headquarters in 1772. They also established subsidiary cities like Bombay and Madras. Calcutta later went on to become 'the second city of the empire after London'. By the 19th century, the British had, one way or the other assumed political control of virtually all of India, though the Portuguese, the Dutch and the French too had their enclaves along the coast. The British would send Indian labourers, policemen and soldiers all over the Empire, resulting in the establishment of Indian diaspora communities, the most notable ones in Myanmar, Malaysia, Singapore, Hong Kong, Fiji, South Africa, Mauritius, Kenya, Guyana, Trinidad and Tobago and the United Kingdom itself.
There was an uprising by Indian rulers in 1857 which was suppressed, but which prompted the British government to take over from the Company and make India a part of the empire. This period of rule by the crown, 1858-1947, was called the British Raj. It was a period in which some Indians converted to Christianity, though forcible conversions ended in British India after 1859, and Queen Victoria's proclamation promised to respect the religious faiths of Indians.
Non-violent resistance to British colonialism led by Mohandas Karamchand Gandhi led to independence on 15 August 1947. However, independence was simultaneously granted to the secular Hindu-majority state of India and the smaller Muslim-majority state of Pakistan, and the orgy of Hindu-Muslim bloodletting that followed Partition led to the deaths of at least half a million and the migration of 12-14 million people.
India achieved self-sufficiency in food grains by the 1970s, ensuring that the large-scale famines that had been common are now history. However these policies also led to shortages, slow growth and large-scale corruption. After a balance-of-payments crisis in 1991, the country adopted free-market reforms which have continued at a steady pace ever since, fueling strong growth. The IT, Business Process Outsourcing and other industries have been the drivers for the growth, while manufacturing and agriculture, which have not experienced reforms, are lagging. About 60% of Indians live on agriculture and around 36% remain in poverty.
Relations with Pakistan have been frosty. The two countries have fought four wars, three of them over the status of Kashmir. The third war between the two countries in 1971 resulted in East Pakistan becoming Bangladesh. India continues to experience occasional terrorist attacks, many of which are widely believed to originate in Pakistan and be ordered or assisted by its military-intelligence complex.
China and India went to war in 1962 over a Himalayan border dispute. Current relations are largely peaceful but tense. There are no land crossings allowed between the two countries, though one border crossing between Sikkim and Tibet was re-opened in 2006 for trade. Security concerns over Pakistan and China prompted India to test nuclear weapons twice (including the 1974 tests described as "peaceful explosions"). India wants to be accepted as a legitimate nuclear power and is campaigning for a permanent Security Council seat.
India is proud of its democratic record. Constitutional government and democratic freedoms have been safeguarded for most of its time as an independent country.
Current concerns in India include corruption, poverty, overpopulation, pollution and forms of environmental degradation, ongoing border disputes with Pakistan and China, cross-border terrorism, and ethnic, political and religious strife which occurs from time to time. India's current obsession, at least among the educated elite, is over whether India will be able to overtake China in economic growth and be an economic and military superpower.
Politics
India is a parliamentary republic and democracy modelled on the British Westminster system. The president, indirectly elected, is the head of state, but this position, while not entirely ceremonial, has limited powers. The prime minister runs the government with a cabinet of ministers, and in practice wields the most authority in government. The parliament is bicameral. The Lok Sabha (House of People), the lower house, is directly elected by universal adult franchise, while the Rajya Sabha (Council of States), or the upper house, is indirectly elected. The Lok Sabha is the more powerful of the two, primarily because a majority in the Lok Sabha is required to form a government and pass budgets, and the prime minister, by convention, is always a member of the Lok Sabha. India has a vast number of political parties. The Hindu nationalist Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP) forms the government, and the centre-left Indian National Congress (known as "Congress") is the main opposition party. India has a strong and independent judiciary and a free press.
India is also a federation, divided into states and union territories. Each of these has its own legislature, with a government run by a chief minister and a cabinet.
Street demonstrations, protests and agitations occur, as they do in any democracy. There are also occasional low levels of political violence, in which a visitor has an extremely small chance of getting caught.
Time zone
Indian Standard Time (IST) is 5 hours and 30 minutes ahead of Co-ordinated Universal Time (UTC+5.5). Daylight Savings Time is not observed in India.
Geography
Mountains, jungles, deserts and beaches, India has it all. It is bounded to the north and northeast by the snow-capped Himalayas, the tallest mountain range in the world. In addition to protecting the country from invaders, they also feed the perennial rivers Ganga, Yamuna (Jamuna) and Sindhu (Indus) on whose plains India's civilization flourished. Though most of the Sindhu is in Pakistan now, three of its tributaries flow through Punjab. The other Himalayan river, the Brahmaputra flows through the northeast, mostly through Assam where it is known by different names. The Manipur River, originated from Manipur, joins the Chindwin-Irrawaddy River System of Myanmar.

The world's only floating lake is the Loktak lake in the central bowl like plain of Manipur. It is remarkably known for its unique circular floating biomasses (Manipuri: Phumdi). It is also the largest lake in the entire Northeast India.
South of Punjab lies the Aravalli range, which cuts Rajasthan into two. The western half of Rajasthan is occupied by the Thar desert. The Vindhyas cut across Central India, particularly through Madhya Pradesh and signify the start of the Deccan plateau, which covers almost the whole of the southern peninsula.
The Deccan plateau is bounded by the Western Ghats range (which is called Sahyadri in Maharashtra) to the west and the Eastern Ghats to the east. The plateau is more arid than the plains, as the rivers that feed the area, such as the Narmada, Godavari and the Kaveri, run dry during the summer. Towards the northeast of the Deccan plateau is what used to be a thickly forested area that covers the states of Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, the eastern edge of Maharashtra and the northern tip of Andhra Pradesh. This area is still forested, poverty stricken and populated by tribal people. This forest acted as a barrier to the invasion of South India.
India has a long coastline. The west coast borders the Arabian Sea and the east coast the Bay of Bengal, both parts of the Indian Ocean.
Climate


In India, it rains only during a specific time of the year. The season as well as the phenomenon that causes it is called the monsoon. There are two of them, the Southwest and the Northeast, both named after the directions the winds come from. The Southwest monsoon is the more important one, as it causes rains over most parts of the country, and is the crucial variable that decides how the crops will do. It lasts from June to September. The Southwest monsoon hits the west coast the most, as crossing the Western Ghats and reaching the rest of India is an uphill task for the winds. The western coastline is therefore much greener than the interior. The Northeast monsoon hits the east coast between October and February, mostly in the form of occasional cyclones that cause much devastation every year. The only region that gets rains from both monsoons is North-Eastern India, which consequently experiences the highest rainfall in the world.
India experiences at least three seasons a year, Summer, Rainy Season (or "Monsoon") and Winter, though in the tropical South calling the 25°C (77°F) weather "Winter" would be stretching the concept. The North experiences some extremes of heat in Summer and cold in Winter, but except in the Himalayan regions, snow is almost unheard of. November to January is the winter season and April and May are the hot months when everyone eagerly awaits the rains. There is also a brief spring in February and March, especially in North India.
Opinions are divided on whether any part of India experiences an Autumn, but the ancients had certainly identified such a season among the six seasons (or ritus - Vasanta - Spring, Greeshma - Summer, Varsha - Rainy, Sharat - Autumn, Hemanta - "Mild Winter"/"late autumn", Sheet - Winter) they had divided the year into.
Culture
|
Culture shock Many visitors expecting maharajas and fabulous palaces are shocked when their first impressions are dominated by poverty instead. Prepare for the following:
Most visitors quickly get inured to these things that are pitfalls of urbanisation and start seeing the good sides too, but take it easy on your first few days and schedule some time to get away from it all. |
India's rich and multi-layered cultures are dominated by religious and spiritual themes. While it is a mistake to assume that there is a single unified Indian culture, there certainly are unifying themes that link the various cultures. India's cultural heritage is expressed through its myriad of languages in which much great literature and poetry has been written. It can be seen in its music, both in its classical (Carnatic and Hindustani) forms and in modern Bollywood music. India also has a vast tradition of classical and folk dances. Art and theatre flourish amongst the bustling cities of the country, against the backdrop of the ever-expanding western influences.
Indians greatly value their family system. Typically, an Indian family encompasses what would be called the extended family in the West. It is routine for Indians to live as part of the paternal family unit throughout their lives, i.e. sons live together with their parents all their lives, and daughters live with their parents till they get married. The relationship is mutually self-supporting. Parents may support their children for longer than is common in the West, brothers and sisters may support each other, and sons are expected to take care of their parents in their old age. "Living with parents" does not carry the same stigma as it does in parts of Europe or North America. Naturally, the arrangements are not perfect and there are strains and breakups, especially by the time the third generation grows up. Also, it has now become common for children to move away from the parental house for education and employment. Nonetheless, it is fair to say that the joint family is still seen as the norm and an ideal to aspire to, and Indians continue to care about their family's honour, achievements and failures even while they are not living together.
Despite the weakening of the caste system (which has officially been outlawed by the Indian government), India remains a fairly stratified society. Indians care more about a person's background and position in society than is the norm in the individualist West. This attitude, when combined with the legacy of colonial rule, results in some rather interesting, if unfortunate consequences. People with white skin are placed high on the societal totem pole, and they may find that Indians are obsequious towards them to the point of embarrassment. People with dark skin, however, may find that they are discriminated against. If it is any consolation, Indians display similar prejudices based on skin colour and ethnicity among themselves and not just towards foreigners. (See more in the Stay Safe and Respect sections)
There is also a community known as the Siddis, who are believed to be descended from East African slaves brought to India by the Arab Slave Trade, and mainly found in remote rural villages. Although they speak Indian instead of African languages these days, they still retain many African customs including African dance and music. Although they are Indian citizens, due to a lack of awareness from the general Indian population of their existence, they continue to face much discrimination, and are often presumed to be illegal immigrants from Africa. The British colonisation also gave rise to a mixed-raced population known as the Anglo-Indians, and while most of them migrated to Western countries following independence, pockets of these communities remain in India's major cities.
Holidays and festivals
There are three national holidays: Republic Day (26 January), Independence Day (15 August), and Gandhi's Birthday, generally called Gandhi Jayanti (2 October) which follow the Western calendar and occur on the same day every year. Hindu religious festivals, because they follow the lunisolar calendar, occur on different days every year, but around the same time of the year every time. The major religious festivals of Islam, Christianity, Sikhism, Buddhism, Jainism and Zoroastrianism are also celebrated. Central government offices are closed for holidays around 17 days a year for these festivals and observances. The significance of these festivals differs across different regions of India. State government offices will have a different holiday schedule based on which festivals are important in that state. Generally, the day on which the state was formed will also be a holiday in that state.
Some of the major Indian festivals are:

- Diwali (Deepavali), Oct-Nov — The festival of lights, celebrates the return of the Hindu God Rama to the capital of his kingdom, Ayodhya after an exile of 14 years and victory of justice over injustice when Narakasura was killed by Satyabhama with the help of Krishna. Probably the most lavish festival in the country, reminiscent of Christmas in Europe or Thanksgiving in the US. Houses are decorated, there is glitter everywhere, and if you wander the streets on Diwali night, there will be firecrackers going off everywhere including sometimes under your feet.
- Ugadhi, [sometimes also called 'Yugadhi' and various other names] is one of the main festivals, which is mainly celebrated as the 1st day of the Hindu Calendar New Year. Which is one of the main festivals and is quite widely followed in South India.

- Durga Puja / Navaratri/Dussehara, Sep-Oct — A nine-day festival culminating in the holy day of Dussehra, when locals worship the deity Durga. Workers are given sweets, cash bonuses, gifts and new clothes. It is also new year for businessmen, when they are supposed to start new account books. In some places like West Bengal and Odisha, Durga Puja is the most important festival. In the north Dussehra celebrations take place and the slaying of Ravana by Lord Rama is ceremonially reenacted as Ram Lila. In Gujarat and South India, it is celebrated as Navaratri where the festival is celebrated by dancing to devotional songs and religious observances like fasts extended over a period of nine nights.
- Holi, in March — The festival of colour is a major festival celebrated mainly in North, East and Western India. On the first day, people go to temples and light bonfires, but on the second, it's a waterfight combined with showers of coloured powder. This is not a spectator sport: as a visible foreigner, you're a magnet for attention, so you'll either have to barricade yourself inside, or put on your most disposable clothes and join the fray. Alcohol and bhang (cannabis) are often involved and crowds can get rowdy as the evening wears on.

- Ganesh Chaturthi, is celebrated all over India. Ganesh Chaturthi is the festival of Lord Ganesh. Ganesh Chaturthi is most enjoyed in Maharashtra. It is the best time to visit cities like Mumbai, Pune, Nagpur.
- Christmas and New Years Day are public holidays across the country and Bank Holidays as well. Christmas is a major festival in the regions of Kerala and Goa.
- Eid-ul-Fitr, Eid-uz-Zuha, Eid-e-Milad-un-Nabi, Yawm-e-Aashoora and Ramazaan are widely celebrated and observed as public holidays across the country.
Apart from these, each state has its own major national festival like Onam in Kerala, Makar Sankranti and Ugadi in Andhra Pradesh, Utarayan in Gujarat, Pongal in Tamil Nadu, Baisakhi for Punjab, Bihu for Assam,Rathayatra(Car festival for lord Jagannath) in Odisha,Nuakhai for Western Odisha. India is a diverse nation, and festivals are a significant part of life for the locals, and they provide holidays for about a week.
Religious holidays occur on different days each year because the Hindu and Islamic festivals are based on their respective calendars and not on the Gregorian calendar. Most of them are celebrated only locally, so check the state or city you are visiting for information on whether there will be closures. Different regions might give somewhat different names to the same festival. To cater to varying religious practices, offices have a list of optional holidays (called restricted holidays by the government) from which employees are allowed to pick two, in addition to the list of fixed holidays. This may mean thin attendance and delayed service even when the office is officially open.
Read
|
Kashmir dispute India and Pakistan have a bitter dispute over Kashmir; each government claims territory that is under the control of the other. They have fought wars over this three times since independence in 1947. Wikivoyage, however, deals only with the current situation on the ground; our maps show and our text describes that without taking sides on the disputes. If you can go there with a Pakistani visa today then we treat it as being in Pakistan, and if you need an Indian visa, we treat it as being in India. This is the most important distinction for travellers. Visitors should exercise considerable caution in these areas. Both governments consider them highly sensitive, keep large military forces along the border, and restrict travel to border areas. |
- An Era of Darkness by Shashi Tharoor. Thought provoking account of how the British Raj impoverished the country and caused humanitarian crises.
- Midnight's Children, Salman Rushdie's allegory about Independence. It was awarded the "Booker of Bookers" Prize and the best all-time prize winners to celebrate the Booker Prize 25th and 40th anniversary. It was also adapted into a film by Indo-Canadian film director Deepa Mehta (2012).
- The India they saw : foreign accounts, by Meenakshi Jain (2011). A compilation of intriguing travel tales and excerpts from travelogues by travellers, writers, pilgrims and missionaries.
- A Goddess in the Stones: Travels in India by Norman Lewis (Cape 1991; US: Holt 1992), In "Goddess in the Stones", influential journalist and author Norman Lewis undertakes a journey of 2500 miles in search of the old India.
- India: A History, John Keay; "A superb one-volume history of a land that defies reduction into simple narrative ... Without peer among general studies, a history that is intelligent, incisive, and eminently readable." (ISBN 0802137970)
- India: A Million Mutinies Now, V.S. Naipaul; "With this book he may well have written his own enduring monument, in prose at once stirring and intensely personal, distinguished both by style and critical acumen (ISBN 0670837024)
- In Spite of the Gods, Edward Luce; an exceptionally insightful and readable book on the unlikely rise of modern India. (ISBN 0316729817)
- No Full Stops In India, Mark Tully; "India's Westernised elite, cut off from local traditions, want to write a full stop in a land where there are no full stops. From that striking insight, Mark Tully has woven a superb series of stories that explore everything from communal conflict in Ahmedabad to communism in Kolkata, from the Kumbh Mela in Allahabad (probably the biggest religious festival in the world) to the televising of a Hindu epic." (ISBN 0140104801)
- Mother Pious Lady, Santosh Desai; An excellent account of middle-class beliefs and customs from the pre-liberalisation era till date. For anyone who wants to understand the culture of present India, this is a must-read where the author cuts through the chaos and confusion letting you see things more clearly. (ISBN 9788172238643)
- Indian journals, March 1962-May 1963: Notebooks, diary, blank pages, writings. Ginsberg, A. (1970). San Francisco: Dave Haselwood Books. Travel diary written by the famous beat poet Allen Ginsberg.
- Lion: A Long Way Home, a book by Saroo Brierley.
- Spiritual India handbook: A guide to temples, holy sites festivals and traditions by Stephen Knapp (2013). Useful for the pilgrim who wants to get the most out of his or her spiritual adventure and experience in India.
See also the Wikivoyage article On the trail of Kipling's Kim.
Touts
Touts are ubiquitous, as in many developing countries, and you should assume that anyone 'proactively' trying to help you has a hidden agenda to part you from your money. However, in areas hardly or not at all visited by tourists, it is not at all uncommon for people who go out of their way to 'proactively' help you when you approach without expecting anything in return. During your travels in India, you will be deluged with touts trying to get you to buy something or patronise particular establishments.
There are a myriad of common scams, which range from telling you your hotel has gone out of business (of course, they'll know of one that's open with vacancies), to giving wrong directions to a government rail ticket booking office (the directions will be to their friend's tour office), to trying to get you to take diamonds back to your home country (the diamonds are worthless crystal), to 'poor students' giving you sightseeing for hours and then with pity make you buy school books for them (tremendously overpriced from a bookstore with whom they are affiliated). There will also be more obvious touts who "know a very good place for dinner" or want to sell you a chess set on the street.
Faced with such an assault, it's very easy to get into a siege mentality where all of India is against you and out to squeeze you dry. This mentality may affect any true appreciation of the country. Dealing with touts is simple: assume anyone offering surprising information (such as "your hotel is shut down") is a tout. Never be afraid to get a second or third answer to a question. To get rid of touts:
- Completely ignore them and go about your business until they go away. This may take quite a while, but patience is key to managing India.
- Tell them "no", very firmly, and repeatedly.
It is also beneficial to have a firm Indian friend whom you can trust. If they show you around, they will act to help you ward off such touts.
Discriminatory pricing
Foreign visitors will quickly encounter the special foreigners' rates that they are charged in some places in India. This applies to many tourist attractions, such as museums and historical sites. The difference in pricing is because the Indian government subsidises entry fees for local people, to make these attractions more affordable for taxpayers. While this may seem discriminatory, it is practised in most developing countries in Asia and Africa and helps make these attractions more accessible to local people.
Some tourist attractions that are run by the Archaeological Survey of India have different rates for Indians and foreigners. These rates are prominently posted at the entrance and ticketing booths. The rates for foreigners may be as many as five to ten times those for Indians. Likewise, if you are reserving a hotel room or an airline ticket over the internet, you may find that paying in euros or US dollars costs significantly more. You can get an Indian friend to book in rupees and in most cases, no one will question you at the time of check in.
Talk
- See also: Hindi phrasebook
At the federal level, the official languages of India are Hindi and English.
Other languages that are official to some degree (often at state level) are Assamese, Bengali, Bodo, Dogri, Gujarati, Kannada, Kashmiri, Konkani, Maithili, Malayalam, Manipuri (also known as Meitei), Marathi, Nepali, Odia (also known as Oriya), Punjabi, Sanskrit, Santhali, Sindhi, Tamil, Telugu and Urdu. There are also hundreds of other less prominent languages like Tulu, Bhojpuri and Ladakhi.

Hindi, spoken by the vast majority of the population, serves as the lingua franca of North India and Central India. Many others have it as their second, or even third language. Although it is one of the main languages of the Union Goverment, very little Hindi is spoken in Southern and Northeastern India, and people in those areas are more likely to respond in English or their local language. There are also over 120 dialects in India. One of them is Haryanvi, which is a common dialect around in Haryana and the Delhi area.
English is spoken in urban areas, and is the main language in education, media, government, and business. It serves as the "de facto lingua franca" of the country. Although this sounds reassuring, Indian English is remarkably different compared to other dialects. Perhaps the most common jibe about the dialect is its use of universally improper grammar, which may give some the impression that India isn't an English-speaking country. Prejudices aside, this is perhaps the dialect's most fascinating quality. The sounds of Indian English are flavoured by many of the country's languages, which means that non-native English speakers may have difficulty understanding the way Indians speak.
Here are some features of Indian English:
- The most commonly used tag question is "isn't it", which can be used to indicate a genuine question (e.g. He is from Tamil Nadu, isn't it?), sarcasm, bewilderment, and so on.
- Nouns are commonly pluralised (e.g. A room full of furnitures, stuffs for eating)
- Verbs conjugate differently (e.g. I knowed about it, I buyed it)
- Colloqualisms, slang words, and idioms are rife, some of which may be perceived as impolite by non-Indians (e.g. Hello, what you want)
- Prepositions and articles are often dropped or combined strangely (e.g. I want computer)
- The use of some vocabulary that would not be said elsewhere (e.g. vote bank which means a group of people that supports a particular political party)
English-language TV shows and movies are common, and the number of English TV channels outnumber the number of Indian-language TV channels. Some shows may be dubbed in another language depending on where you are.
Sanskrit is the language in which much of ancient Indian literature and religious texts are written. Today Sanskrit survives primarily as a liturgical language; few if any people speak Sanskrit as a native language, but quite a few scholars or lay-persons know it or are learning it. Many modern Indian languages are descended from Sanskrit, and even those unrelated to Sanskrit have been strongly influenced by it.
While most north Indian languages, including Hindi, are descended from Sanskrit, the main languages of the south — Telugu, Tamil, Kannada and Malayalam — originate from a different language and are called the Dravidian languages. Ironically, Telugu, Kannada and Malayalam are far more Sanskritic than Hindi due to the relative absence of Islamic rule in those regions. In Northeast India, Meitei (popularly called Manipuri) is a language of Sino-Tibetan family, that has more closeness towards Chinese, Burmese and Tibetan, making herself unique from other major Indian speeches.
However, you are better off picking up as many words as you can of the local language of the place you are going to - people are proud of their state's (or region's) culture and language and will appreciate it if an outsider makes an attempt to communicate in it. Code-switching between English and the local language (often given a portmanteau of the native language and English; for instance, mixing Malayalam and English is called as Manglish, and the same for Hindi is called as Hinglish) is common among the youth in urban areas, although most educated people would speak standard English (British) when talking to foreigners.
Many Indian languages lack a word for please, just like the Scandinavian languages. Instead, verbs have many forms denoting levels of politeness and formality. As there is no such distinction in English, Indians may also seem commanding to a westerner. You may hear phrases like come here which may sound commanding to Anglophones from Western cultures, but this is not meant to be rude.
Non-verbal communication is also important. Much has been made of the confusing Indian head nod for yes and no, but the only important thing to understand is that Indians have different nods for yes, ok and no.
- If they are nodding their head up and down, they mean yes or I agree, as in a standard nod.
- If they are shaking their head in a tilting motion from right to left and back, they mean I understand or I get what you said.
- If they shake their head sideways (left to right to left), they mean no.
- There are differences in the way these signs are used in northern and southern India. The back to forth is yes and a vigorous left-right shift is no in northern India, though the latter may be construed for yes in southern states like Tamilnadu. Look for verbal cues that accompany these sounds (like 'aaan' for yes ) in southern India to get the correct meaning.
Get in

|
Visa restrictions:
Certain states in India require permits to visit. Citizens of Bangladesh, Pakistan, China, and Myanmar are not usually eligible for them unless they have permission from the Home Ministry.
|
Entry requirements
Visas

Rules and validity of visas will differ based on citizenship. Check the website of the Indian embassy, consulate or high commission in your country, found on this list.
Holders of an Overseas Citizenship of India (OIC) document are permitted to live in India indefinitely, however they must apply for permits to visit certain areas in India.
Citizens of Nepal and Bhutan may enter and live in India indefinitely without a visa.
Citizens of Maldives may stay up to 90 days without a visa.
Citizens of Japan, South Korea, and the United Arab Emirates are eligible for visas on arrival may stay up to 60 days without a visa.
Citizens of Pakistan, including dual citizens, not only require a visa, but they also require clearance from the Indian government. Citizens of Pakistan are rarely granted visas of any kind and it can take several years to get a clearance from the Indian government. Pakistani citizens over the age of 65 can apply for a visa on arrival, but they are ineligible for the scheme if they've been denied an Indian visa in the past.
Depending on the purpose of the visit, with most passports you can get a tourist visa (multiple entry for six months or one year depending on nationality), a business visa (6 months, one year or more, multiple entries) or a student visa (up to 5 years). A special 10-year visa is available to nationals of certain countries, including U.S. citizens (US$100). An Indian visa is valid from the day it is issued, not the date of entry. For example, a 6-month visa issued on 1 January will expire on 30 June, regardless of your date of entry. (This is not true for e-Visas, which are valid 60 days "from the date of arrival in India."—see the "Instructions for Applicant" section of the e-Visa page.)
|
Do you need a visa? Yes, (except for 3 countries) Electronic Tourist Visa (eTV) regulations cover entry into India through certain airports from certain countries. See this webpage for more details. eTV allows double entry, for stays up to 60 days, non-extendable and non-convertible. It is not possible to obtain eTV at land crossings. You must arrive at one of the following airports or seaports for your first entry: Airports: Ahmedabad, Amritsar, Bagdogra, Bangalore, Calicut, Chennai, Chandigarh, Cochin, Coimbatore, Delhi, Gaya, Goa, Guwahati, Hyderabad, Jaipur, Kolkata, Lucknow, Mangalore, Mumbai, Nagpur, Pune, Tiruchirapalli, Trivandrum, and Varanasi. Seaports: Cochin, Mangalore, and Goa. Second entry allowed at all entrance points. If you do not want the restrictions of the eTV, you must get a regular visa. For U.S. passport holders, you must start your visa application here. VFS Global Visa-exempt
e-Tourist visa (eTV)
Advance visa required
Visa required with a minimum of 4 weeks waiting time
Visa required with a minimum of 45 days waiting time
|
India has an e-Tourist Visa (eTV) facility. Electronic visas can be applied for between 4 and 120 days in advance of arrival and are valid for a double entry and a stay of up to 60 days. Travellers cannot receive more than two eTVs in a calendar year. Entry with an eTV must be at 1 of 25 designated airports (Ahmedabad, Amritsar, Bagdogra, Bangalore, Calicut, Chennai, Chandigarh, Cochin, Coimbatore, Delhi, Gaya, Goa, Guwahati, Hyderabad, Jaipur, Kolkata, Lucknow, Mangalore, Mumbai, Nagpur, Pune, Tiruchirapalli, Trivandrum, Varanasi, Vishakhapatnam - check the web link for a current list). The eTV is available to citizens of over 100 countries (again, check the web link for the latest list; some EU countries, along with most of Africa and the Middle East, are excluded). Persons of Pakistani origin, regardless of nationality, are not eligible. The fee for the eTV is dependent on nationality. Since 2019 e-Visas are issued for 30 days, 1 year or 5 years. The 1-and-5 year visas allow stays for up to 60 days at a time (except for nationals of the US, UK, Canada and Japan, who are allowed to stay for 90 days). Also, prices are expected to go down, and there will be no limit on the number of e-visas you can request in a calendar year. The exact implementation date is still not known.
The eTV facility replaced the limited visa-on-arrival scheme in January 2015; there are no longer any visa-on-arrival facilities in India.
Regular visa applications for U.S. passport holders (for travellers not eligible for eTV) begin at VFS Global before being submitted to a visa application centre either by FedEx or in person.
Many Indian embassies have outsourced visa processing in full or in part to third party companies, so check ahead before going to the embassy. For example, in the USA as of 9 Oct 2020, your visa application must be submitted to VFS Global rather than the embassy. Applications through these agencies also attract an application fee (in the US to VFS Global, this fee is USD15.90) above that which is detailed on most embassy websites and should be checked prior to submitting your paperwork. In addition, many Indian embassies only offer visas to residents of that country: this means you should get your visa before you leave home instead of trying to get it in a neighbouring country (although, as at August 2009, non-residents are able to apply for visas through the Bangkok embassy for an additional 400 THB "referral fee").
It's wise to ask for a multiple-entry visa even if you aren't planning to use it - they cost the same, are handed out pretty liberally and come in handy if you decide last minute to dip into one of the neighbouring countries.
A business visa may be required if you intend to do anything work related in India. The eTV does permit 'casual business visits' and will be easier to obtain. If you do need a business visa, then be prepared to provide a great deal of documentation about your company in your home country as well as the company you are visiting in India. This will include (but may not be limited to) an invitation letter from the company that you are visiting as well as business registration documents and possibly tax returns and other sensitive documents. It may be worth applying for a short-term visa (such as 6 months) since the criteria may be less in your case.
There are other categories for specialised purposes. The missionary visa is mandatory for anyone who is visiting India "primarily to take part in religious activities". This rule is meant to combat religious conversion, particularly of Hindus to Christianity. There have been cases where preachers have been deported for addressing religious congregations while on a tourist visa. You don't need to be worried if you are just on a religious tour of churches in India.
If you are on a Student, Employment, Research or Missionary visa, you need to register within 14 days of arrival with the Foreigners Regional Registration Office where you will be staying. If the place you are staying at doesn't have one, you need to register at the local police station. All visitors who intend to stay more than 180 days also need to be registered.
Overstaying a visa is to be avoided at all costs as you will be prevented from leaving the country until you have paid some fairly hefty fines and presented a large amount of paperwork to either the local immigration office or police station. This whole process is unlikely to take less than 3 days, and can take much longer if you include weekends, numerous government holidays and the inevitable bizarre bureaucratic requirements. In the worst-case scenarios, the Indian Government can also take legal action for exceptionally long overstays including prison term for 5 years.
Penalties for overstaying in India
- For Overstays or non-registration for up to 90 days, penalty is US$300.
- For Overstays from 91 days to 2 years, penalty is US$400.
- For Overstays more than 2 years, penalty is US$500.
Penalties for overstay in India may differ for persons belonging to minority communities from nearby countries like Pakistan, Bangladesh, and Afghanistan:
- For Overstays or non-registration for up to 90 days, penalty is ₹100
- For Overstays from 91 days to 2 years, penalty is ₹200
- For Overstays more than 2 years, penalty is ₹500
Customs and immigration
Clearing customs can be a bit of a hassle, though it has improved vastly over the last decade. In general, avoid the touts who will offer to ease your baggage through customs. There are various rules regarding duty-free allowances — there are differing rules for Indian citizens, foreign "tourists", citizens of Nepal, Bhutan and Pakistan, non-citizens of Indian origin and people moving to India. Use the website of the Central Board of Excise and Customs for information about what you can bring in. Foreign tourists other than Nepalis, Bhutanese and Pakistanis and those entering through Nepal, Bhutan or Pakistan, are entitled to bring in their "used personal effects and travel souvenirs" and ₹4,000 worth of articles for "gifts". If you are an Indian citizen or are of Indian origin, you are entitled to ₹25,000 worth of articles (provided you aren't entering through Nepal, Bhutan or Pakistan). The other rules are on the web site. If you are bringing any new packaged items, it is a good idea to carry the invoices for them to show their value. You are also allowed to bring in 200 cigarettes or 50 cigars or 250 grams of tobacco and 1 litre (2 litres for Indians) of alcohol duty-free. If you do not have anything to declare, you can go through the green channel clearly marked at various airports and generally you will not be harassed.
Importing and exporting Indian rupees is strictly forbidden for foreigners, and limited to ₹25000 for Indian citizens. Details can be found in the official statement of the Reserve Bank of India. There are currency exchange counters at international airports where you are required to change all your excess Indian rupees to foreign currency before leaving.
By plane

The major points of entry are Bangalore (BLR IATA), Mumbai (BOM IATA), Delhi (DEL IATA), Kolkata (CCU IATA), Hyderabad (HYD IATA) and Chennai (MAA IATA). The airports at these cities are either new or undergoing development. The Hyderabad airport is rated as one of the top five airports in the 10-15 million passenger category. There are many nonstop, direct and connecting choices to these cities from Europe, North America, Middle East, Africa and Australia.
Secondary points of entry include Goa and the Malabar coast. There are many connections from the Middle East to Malabar coast cities such as Kochi, Kozhikode and Thiruvananthapuram. Most of the major Middle Eastern carriers offer one-stop connections to the coast from their Gulf hubs. Goa is a favourite European tourist destination and thus is connected by many European charter operators like Condor, Edelweiss and Thomson Airways.

India's national airline is Air India. Other Indian airlines that operate international flights include IndiGo and SpiceJet. These airlines offer daily flights to major hubs around the world. You must carry a printed air ticket in order to take many domestic flights.
From the United States, United Airlines offers non-stop daily service from Newark to Delhi and Mumbai; Air India offers daily non-stop service to Delhi from New York–JFK, Newark, Washington–Dulles, San Francisco and Chicago O'Hare and to Mumbai from Newark (and soon JFK). Various European airlines offer connecting service through their European hubs from most major U.S. cities and various Asian airlines offer connecting service from West Coast cities through their Asian hubs.

Entries from Europe and North America are possible using many European airlines such as Lufthansa, Finnair, British Airways, KLM, Air France and Virgin Atlantic. For long-term visitors (3–12 months), Swiss Airlines often have good deals from Switzerland with connecting flights from major European and some American cities as well.
To save on tickets, consider connecting via Gulf countries, with Air Arabia (Sharjah-based low cost carrier with some connections to Europe), Etihad (especially if you need a one-way ticket or are going back to Europe from another Asian country) via Abu Dhabi, Emirates via Dubai or Qatar Airways via Doha. These airlines are also the easiest way to come from the Gulf countries, along with Indian carriers, Air India, Air India Express, Indigo and SpiceJet.
From East Asia and Australia, Singapore (which is served by Air India, its low-cost subsidiary Air India Express, Singapore Airlines, its subsidiary Silk Air and low-cost subsidiary Scoot) has excellent connections with flights to all the major cities and many smaller ones. As for the cheap way from Southeast Asia, Malaysian low-cost carrier AirAsia is often the best choice (if booked well in advance, one-way ticket price is normally below US$100, sometimes being less than US$50, they have connections from China, Australia and most South-east Asian countries). They fly from Kuala Lumpur into New Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, Kolkata, Kochi and Tiruchirapalli. If you're going from Thailand, Air India Express flies from Chennai and Kolkata to Bangkok. Air India and Thai Airways fly from there to a range of Indian cities as well. Silk Air flies from Singapore to Hyderabad as well. IndiGo, an Indian low-cost-carrier, also offers attractive fares to Singapore and Bangkok.
By boat
India has several international ports on its peninsula. Kochi, Mumbai, Goa and Chennai are the main ones handling passenger traffic, while the rest mainly handle cargo. However, due to the profusion of cheap flights, there no longer appear to be any scheduled ferry services from India to the Middle East. The southern island of Minicoy in Lakshadweep islands is now a permitted entry point.
Some cruise lines that travel to India include Indian Oceans Eden II and Grand Voyage Seychelles-Dubai.
By train
There are two links from Pakistan. The Samjhauta Express runs from Lahore to Attari near Amritsar in Punjab. The Thar Express, restarted in February 2006 after 40 years out of service, runs from Munabao in the Indian state of Rajasthan to Khokrapar in Pakistan's Sindh province; however, this crossing is not open to foreign tourists. Neither train is the fastest, safest or the most practical way to go between India and Pakistan due to the long delay to clear customs and immigration (although the trains are sights in their own right and make for a fascinating trip). Ths Samjhauta express was the victim of a terrorist strike in February 2007, when bombs were set off killing many people. Should you want to get from one country to the other as quickly as possible, walk across at Attari/Wagah.
From Nepal, trains run between Khajuri in Dhanusa district of Nepal and Jainagar in Bihar, operated by Nepal Railways. Neither is of much interest for travellers and there are no onward connections into Nepal, so most travellers opt for the bus or plane instead.
Train services from Bangladesh were suspended for 42 years, but the Moitree Express started running again between Dhaka to Kolkata in April 2008. The service is biweekly: A Bangledeshi train leaves Dhaka every Saturday, returning on Sunday, while an Indian train leaves Kolkata on Saturdays and returns the next day.
You can see what trains are available between stations at the following sites: http://www.indianrail.gov.in. However, for booking of rail tickets through the internet you should use the Government of India's website http://www.irctc.co.in. For booking through this site, you have to register (which is free) and you need a credit/debit card. You can also take the services of many travel agents that charge a nominal service fee for booking train tickets.
By land

Nepal
From Nepal buses cross the border daily, usually with connections to New Delhi, Lucknow, Patna and Varanasi. However, it's cheaper and more reliable to take one bus to the border crossing and another from there on. The border crossings are (India/Nepal side) Sunauli/Bhairawa from Varanasi, Raxaul/Birganj from Patna, Kolkata, Kakarbhitta from Darjeeling, and Mahendrenagar-Banbassa from Delhi.
Bhutan
The Royal Bhutanese Government runs a service to/from Phuentsholing. These buses depart from Kolkata's Esplanade bus station at 7PM on Tuesday, Thursday and Saturday and from the Phuentsholing Bhutan Post office at 3PM on Monday, Wednesday and Friday. The journey takes around 18 hours and costs ₹300. The buses are comfortable, but because much of the highway to Kolkata is like the surface of the moon, don't bank on getting much sleep on the way.
There is frequent service between Siliguri and Phuentsholing.
Myanmar
Entering from Myanmar is apparently possible at Moreh/Tamu—see Myanmar article for more details. Regarding Indo-Myanmar connection, Manipur is the most advanced and the only developed route inside India, to pass to and from between the two nations.
Pakistan
From Pakistan the only land crossing is from Lahore to Amritsar via the Attari/Wagah border crossing. Despite tensions between the two countries, there is a steady trickle of travellers passing this way. The immigration procedures are fairly straightforward, but neither Pakistan nor India issue visas at the border. Expect to take most of the day to go between Lahore and Amritsar on local buses. Normally it's possible to get a direct bus from Amritsar to the border, walk to the other side and catch a direct bus to Lahore, although you may need to change at some point on route. Amritsar and Lahore are both fairly close to the border (about 30–40 minutes drive), so taxis are a faster and easier option.
The direct Delhi-Lahore service has restarted, though it is far more costly than local buses/trains, not any faster, and would mean you miss seeing Amritsar. You will also be stuck at the border for much longer while the bus is searched and all of the passengers go through immigration.
There is now a bus service across the 'Line of control' between Indian and Pakistani Kashmir; however, it is not open to foreign tourists.
For going by car also see Istanbul to New Delhi over land. You will need a Carnet de Passage if crossing with your own vehicle. The process is not particularly lengthy - crossing with your own vehicle from/to Pakistan should take a maximum of 3 hours to clear both borders for you and your vehicle.
From Bangladesh
From Bangladesh there are a number of land entry points to India. The most common way is the regular air-conditioned and comfortable bus services from Dhaka to Kolkata via Haridaspur (India)/Benapole (Bangladesh) border post. Bus companies 'Shyamoli', 'Shohag', 'Green Line' and others operate daily bus services under the label of the state owned West Bengal Surface Transport Service Corporation (WBSTSC) and the Bangladesh Road Transport Corporation (BRTC). From Kolkata 2 buses leave every Tuesday, Thursday, and Saturday while from Dhaka they leave on Monday, Wednesday and Friday. The journey usually takes around 12 hours with a one-way fare of ₹400-450 or BDT600-800, roughly US$8–10.
Another daily bus service by 'Shyamoli' and others under the BRTC label from Dhaka connects Siliguri, but the buses in this route do not cross the Changrabanda/Burimari or Burungamari border post. Rather, passengers reaching the border have to clear customs, walk a few hundred yards to cross the border and board the awaiting connecting buses on the other end for the final destination. Ticket for Dhaka-Siliguri-Dhaka route costs BDT 1,600, roughly US$20–25 depending on conversion rates. Tickets are purchased either in Dhaka or in Siliguri.
There is also a regular bus service between Dhaka and Agartala, capital of Tripura. Two BRTC buses daily from Dhaka and the Tripura Road Transport Corporation plying its vehicles six days a week with a round fare costing US$10 connect the two cities. There is only one halt at Ashuganj in Bangladesh during the journey.
Other entry points from Bangladesh are Hili, Chilahati/Haldibari, Banglaband border posts for entry to West Bengal; Tamabil border post for a route to Shillong in Meghalaya, and some others with lesser known routes to north-eastern Indian regions.
China
The Nathu La pass in Sikkim, which borders Tibet in China is the only border crossing between India and China. This border is not open to tourists; only local traders are allowed to cross. Special permits are required to visit the pass from either side, and foreigners are not permitted to visit the Indian side of the border.
Get around
India is big and there are lots of interesting ways to travel around it, most of which could not very well be described as efficient or punctual. Allow considerable buffer time for any journey with a fixed deadline (e.g. your flight back), and try to remember that getting there should be half the fun.
Travel in much of the North-East (with the notable exception of Assam) and parts of Andaman and Nicobar, Jammu and Kashmir, Lakshadweep, Rajasthan, Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand will require obtaining a Protected Area Permit (PAP). The easiest way to get one is to request it along with your visa application, in which case it will be added to your visa. Otherwise, you will need to hunt down a local Ministry of Home Affairs office and battle with bureaucracy.
By plane

India's large size and uncertain roads make flying a viable option, especially as prices have tumbled in the last few years. Even India's offshore islands and remote mountain states are served by flights. Due to the aviation boom over the last few years, airports have not been able to keep up with the air traffic. Most Indian airports continue to function with one runway and a handful of boarding gates. Check-in and security queues can be quite long, especially in Delhi and Mumbai. India has built two new international airports in Hyderabad and Bangalore, which are modern and well-equipped. Delhi airport's newly constructed Terminal 3 is the 8th largest terminal in the world.
In northern India, particularly Delhi, heavy winter fog can wreak havoc on schedules, especially during Christmas Season and January, leading to massive delays across the country. Flights to small airports up in the mountains, especially to Leh in Ladakh (which is reachable only by plane for most of the year), are erratic at the best of times.
Airlines
At one time, domestic flights were the monopoly of the government-owned Indian Airlines, but things have changed dramatically and now there are quite a few competitors, often offering excellent value . The main operators are:
- Air India, India's state-owned flag carrier. Air India has a wide network in the country and provides excellent regional connectivity. Service is generally below par. Their services have been quite a few times in the past been affected by pilots' strikes. Air India also operates a low-cost carrier Air India Express, which flies mainly on trunk routes and to international destinations in the Gulf and South-East Asia, and Alliance Air, which flies small aircraft to obscure places.
- IndiGo - low-cost airline, connecting around 33 cities throughout the country. Their planes are new A320s purchased directly from Airbus a few years ago at most.
- Go First, another low-cost carrier connecting around 22 cities across the country. Mostly flies from their Mumbai base.
- SpiceJet, a third low-cost airline, serves around 34 domestic destinations.
- Air Asia India, newly-launched low-cost service airline
- Vistara, full-service airline
Fares
The earlier you book, the lower you pay. You will hear a lot about air tickets at ₹500, but those are promotional rates for limited seats which are sold out within seconds. In some other cases, the advertised fare may not include charges such as passenger service fees, air fuel surcharge and taxes which will be added subsequently. Nonetheless, you do get good rates from budget airlines. Tickets for small cities will cost more than those for the metros, because of the spotty coverage noted above. Indian ticket pricing has not attained the bewildering complexity that the Americans have achieved, but they are getting there. You don't have to worry about higher prices on weekends, lower prices for round-trips, lower prices for travel around weekends.
There are two complications for non-Indians trying to buy plane tickets:
- Many airlines have higher fares for foreigners than for Indians. Foreigners ("non-residents") will be charged in US dollars, whereas Indians will be charged in rupees. In practice, you can simply pretend to be Indian when booking online as the check-in desk will rarely if ever care, but you are still running a small risk if you do this. When possible it's best to patronise those airlines that do not follow this practice.
- Many online booking sites and some of the low-cost carriers reject non-Indian credit cards. Read the small print before you start booking, or book directly with the airline or through a bricks-and-mortar travel agency instead.
Check in
Checking in at Indian airports tends to be slow, involving lots of queues and multiple security checks. A few pointers to smooth your way:
- Arrive at least two hours before departure if travelling from the major airports. (For domestic flights from minor airports, 60 or 90 minutes before is fine.) The new rule dictates that check-in closes 45 minutes before departure time and the boarding gate closes 25 minutes before departure. Though the original boarding might take longer, this rule is now being strictly implemented widely to avoid delays in flight departures.
- Bring a print-out of your ticket or a soft copy of your ticket and a government-issued id, or else you are not allowed to enter the airport. They are checked and matched compulsorily at the airport entry gate by security guards. If you possess neither a printout or a soft copy, you can get a copy at the airline offices just outside the airport entry gate. Some airlines have started to charge for this privilege.
- Most older airports require that you screen your checked bags before check-in, usually at a stand near the entrance. In high-security airports like Jammu, Srinagar or anywhere in the Northeast, even carry-on baggage needs to be screened. All carry on baggage will be screened by an X-ray scanner and at the discretion of the security personnel, physically too.
- Pick up a tag for every item of carry-on baggage and attach it to it. The staff at the security checkpoint will stamp your boarding pass as well as the tags of your carry-on baggage. Do not put your boarding pass on the X-ray belt, bring it with you when you go through the metal detector. Make sure you received all these stamps before leaving the security check area. Without a stamped boarding pass you will not be allowed to board the plane. You will not be allowed to take any items onboard without a stamped tag attached.
Don't hesitate to ask someone if you are unsure. Most staff in airports are very helpful to passengers and will take pains to ensure you catch your flight. There are separate queues for passengers travelling light (without check-in baggage) and these queues are usually less crowded. Different airlines have different standards for what they allow as cabin baggage, so err on the side of caution, especially if you are travelling by a low-cost airline. Usually, the allowed free baggage limit is 15 kg on most airlines.
By train

| COVID-19 information: Due to the coronavirus pandemic, services may be reduced due to local lockdowns and curfews. | |
| (Information last updated 05 Jan 2022) |
- See also: Rail travel in India
Railways were introduced in India in 1853, more than one and half a century ago by the British, and today India boasts of the biggest network of railway lines in the world, and the rail system is very efficient, if rarely on schedule. Travelling on Indian Railways gives you the opportunity to discover first hand the landscape and beauty of India, and is generally more economical than flying domestic. It is one of the safest ways of travel in India. With classes ranging from luxurious to regular, it's the best way to get to know the country and its people. Most train passengers will be curious about you and happy to pass the time with a chat. While taking an overnight sleeper train will save the money you'd otherwise spend on a hotel, your sleep may not be as comfortable.

Regular trains
Trains come in many varieties. Most express and passenger trains operate with ICF coaches. ICF coaches are now slowly being replaced with LHB coaches. The 'Rajdhani' & 'Shatabdi' trains are the most luxurious and fastest trains on Indian Railways. They are completely air-conditioned and have breakfast, lunch, evening tea and dinner included in your ticket price. The food is served at your seat during travel. Almost all of these trains also have modern German designed LHB coaches which are extremely comfortable and luxurious. 'Vande Bharat Express', a semi-highspeed train was introduced in 2019 and is aimed to replace all 'Shatabdi' trains. It is equipped with onboard Wi-Fi, infotainment, reading lights and electric outlets.
The 'Garib Rath' literally means the chariot of the poor, and it is a good option for those who want to use good facilities at low cost.
Luxury trains
There are 5 trains offering 12 signature journeys between major tourist destinations in India. They offer a wonderful way to experience the sights in India without having to worry about the hassles of travel and accommodation. Journeys on board these trains are all inclusive of accommodation, dining, sightseeing, transportation and porter charges. Each of these luxury trains is equipped with amenities such as live television, individual climate control, restaurant, bar, lounges and cabins with electronic safe and attached bathrooms.
Classes
India has seven classes of train travel to choose from. Not all classes are available on all trains: for example, Chair Cars are usually found only on short-distance daytime trains, while sleeper classes are only found on overnight journeys.
Full information about this classes is here.
Different types of trains
Basically there are five types of trains:
- Passenger Trains are slow trains that stop in all stations including very small stations.
- Fast Passenger Trains are passenger trains that skip smaller stations and offer the same fare structure.
- Express Trains stop only at major railway stations and charge higher than Passenger trains.
- Superfast Trains skip some of the major stations and charge even higher than Express Trains.
- Rajadhani and Shadabdhi Trains are elite trains that offer only air conditioned coaches. They stop only at selected stations. The fare is quite high because all food is included.
Train fare
The average fare for a 200 km distance for different classes is given below:
- First Class AC: ₹1,200
- Two Tier AC: ₹617
- Three Tier AC: ₹430
- AC Chair Car: ₹203
- Sleeper Class: ₹120
- Second class seat in Express train: ₹70
- Second class seat in Passenger train: ₹30
Ticketing
Trains tend to fill up early. Tickets can be reserved up to 4 months in advance. School summer vacation time — mid-April to mid-June — is peak season for the railways, which means that you may need to book well in advance. Other festival days, long weekends or holidays may see a similar rush.
Booking tickets from the railway website has vastly improved over the years. A lot of work has gone into the usability and responsiveness of the website.
Tickets are also available from counters at most railway stations. Details of facility available for tourists from abroad are available at IRCTC website and Indian Railway Website

One day before the departure date of a train the Tatkal quota seats become available. Tatkal accounts for about 10% of the total number of seats. This allows tourists who like to plan a trip as they go to book seats closer to the day of departure, for an extra fee. However, booking for this service online or in person is an even more fraught experience.
It is sometimes difficult to book Tatkal tickets online because of the excess amount of traffic on Indian railway website. Indian railway has launched E-wallet facility which enables users to keep money on Indian railway website for faster booking of tickets. This facility reduces the time of ticket booking because users skip the payment gateway processing time. It is very fast to book tickets using E-wallet facility. You may also need IFSC Code to transfer funds to the E-wallet, but now you can also pay using your debit cards, credits cards, internet banking, etc. IFSC Code generally stands for Indian Financial System code which uniquely identifies bank branches in India, IFSC code is required to transfer money online in India. You can easily find IFSC Code using IFSC Code finder
Meals
Most long-distance night trains (though not all) have a pantry car and if you are in the sleeper or air-con classes, you can buy meals onboard the train. The pantry staff will visit your seat before meal timings to take down your order. However, most pantry car meals aren't really good in quality or taste. The railways are concerned about the bad quality of pantry car meals and efforts are underway to improve things, but do not count on it as yet. If you are finicky, bring enough food for the journey including delays: bananas, bread, and candy bars are good basics. You can purchase drinks, packaged snacks or biscuits from the pantry staff who circulate from one coach to another.
At most stations, hawkers selling tea, peanuts, and snack food and even complete meals will go up and down the train. Most stations will have vendors selling all kinds of edible stuff. You can also get down on the station platform to look for food, but make sure you know the stoppage timing of the train at that station. In the most luxurious 'Rajdhani' & 'Shatabdi' trains, meals are included in your ticket price and served at your seat during travel. There are no dining cars in Indian Railways except in select luxury trains.
By taxi or ride-hailing
|
Farewell to the King Once upon a time, virtually all Indian taxis were trusty Hindustan Ambassadors, a locally manufactured copy of the 1950s-vintage Morris Oxford, but these days the King of Indian Roads is an endangered species.  |
There was a time when the metered taxi was unheard of outside India's largest cities, and when it could be found, getting one that would take you to your destination and charge you the right rate was a rare event. This situation has undergone a drastic change for the better in the past few years, with many online companies offering taxi services. The two largest players are Ola and Uber, both of which operate in all major Indian cities and have ranks at major airports. Both pickup and dropoff points can be entered in English, minimising hassle.
Fares are affordable by Western standards, with most city rides under ₹200, although surge pricing can be expensive. However, the very cheapest categories (UberX and Ola Micro/Mini respectively) often have tiny, run-down cars, so paying the small premium for the next class up (Uber Comfort and Ola Prime) may be worth it.
If ride-hailing isn't an option, central locations of big cities like airports or stations have pre-paid taxi services managed by local traffic police officials. However, beware of touts who would claim themselves to be running pre-paid taxis. Always collect the receipt from the counter first. The receipt has two parts: one part is for your reference and the other part you will need to be handed to the taxi driver only after you reach your desired destination. The taxi driver will receive their payment by submitting or producing this other part to the pre-paid taxi counter. The taxi driver may not know how to get to your destination, and will not tell you this beforehand. This may result in the taxi stopping at various points during the journey as the driver gets out to ask for directions. Insist on being taken to your original destination, and not a substitute offered by the driver (e.g. a different hotel).
Regular metered taxis are also common and can usually be hailed on the street. While they're supposed to use the meter, tales of "broken" meters and hapless fleeced tourists are common, so try to have an idea of the fare before you set off.
By bus

While you can't take a cross-country bus journey across India, buses are the second most-popular way of travelling across states and the only cheap way of reaching many places not on the rail network (e.g. Dharamsala).
Every state has its own public bus service, usually named "X Road Transport Corporation" (or XRTC) or "X State Transport Corporation" (or XSTC) which primarily connects intrastate routes, but will also have services to neighbouring states. There are usually multiple classes of buses. The ordinary buses (called differently in different states, e.g. "service bus") are extremely crowded with even standing room rarely available (unless you're among the first onboard) as reservations are not possible and they tend to stop at too many places. On the upside, they're very cheap, with even a 5-6 hour journey rarely costing over ₹100.
In addition to ordinary public buses, there are luxury or express buses available, and most have air-conditioning these days. Some state transport corporations have even introduced Volvo buses on some routes and these are extremely luxurious and comfortable. These better class "express" or "luxury" buses have assured seating (book in advance), and have limited stops, making them well worth the slight extra expense. But even these better-class buses rarely have toilets and make occasional snack and toilet breaks.
Private buses may or may not be available in the area you are travelling to, and even if they are, the quality could vary a lot. Be warned that many of the private buses, especially long-distance lines, play music and/or videos at ear-splitting volume. Even with earplugs it can be nerve-wracking. Restrooms are available in large bus stations but are crowded. The bus industry is extremely fragmented and there are few operators who offer services in more than 2 or 3 neighbouring states. Travel agents usually only offer seats on private buses.
However, long distance bus operators such as Raj National Express and KPN Travels are rolling out their operations across the country modelled on the lines of the Greyhound service in the United States. Their services are good and they provide entertainment on board.
Regardless of the class of travel, all buses have to contend with the poor state of Indian highways and the havoc of Indian traffic which usually makes them slower, less comfortable and less safe than trains. Night buses are particularly hazardous, and for long-distance travel it's wise to opt for sleeper train services instead.
By car
Our itinerary article Grand Trunk Road describes one of India's major roads, running east-west through the Ganges valley and west across northern Pakistan to Kabul.
Driving on your own
In India driving is on the left of the road — at least most of the time. You can drive in India if you have a local licence or an International Driving Permit, but unless you are accustomed to driving on extremely chaotic streets, you probably will not want to. The average city or village road is narrow, often potholed and badly marked. National Highways are better, but they are still narrow, and Indian driving discipline is non-existent. In the past few years the Central government has embarked on an ambitious project to upgrade the highways. The Golden Quadrilateral connecting the four largest cities of Chennai, Mumbai, Delhi and Kolkata with four-laned highways has been completed and is of a reasonable standard. Some of it is of an international standard but that cannot be said for all of it. However, improving the quality of the roads does not improve the way in which people drive and it is very dangerous to drive on the roads in India as people drive as they like without regard to any rules (rules do exist but are almost never enforced).
Hiring driver with car

Instead, you can opt for a driver while renting a car. Rates are quoted in rupees per kilometre and you will have to pay for both ways even if you are going only one way. The driver's salary is so low (typically around ₹100-150 per day) that it adds little to the cost of renting the car. The driver will find their own accommodation and food wherever you are travelling, although it is customary to give him some money to buy some food when you stop somewhere to eat. Rates vary by size and quality of the car. Many vehicles come equipped with a roof carrier, so one may opt for a smaller vehicle for 2-3 passengers even with excess luggage. (You may need to specifically ask for a vehicle with a roof carrier.)
There are numerous advantages to having a car and driver.
- A good local driver is the safest means of car travel.
- You can keep your bags and shopping goods with you securely wherever you go.
- The driver will often have some knowledge of local tourist destinations.
- The car is at your disposal. You needn't spend any time finding further transport, or haggling over price.
It is rare to find a driver that speaks more than a few words of English. As a result, misunderstandings are common. Keep sentences short. Use the present tense. Use single words and hand gestures to convey meaning.
Make sure you can trust your driver before you leave your goods with him. If he shows any suspicious behaviour make sure you keep your bags with you.
Your driver may in some cases act as a tout, offering to take you to businesses from which he gets baksheesh (a sort of commission). This isn't necessarily a bad thing - the driver may help you find just what you're looking for, and add to his income at the same time. On the other hand, always evaluate for yourself whether you are being sold on a higher-cost or poorer quality product than you want. Avoid touts on the road posing as guides that your driver may stop for because he gets a commission from them; supporting them only promotes this unpleasant practice. The driver might ask for a tip at the end of the trip. Pay him some amount (₹100/day is generally sufficient) and don't let him guilt-trip you into paying too much.
Memorise your driver's face and write down his licence plate number and phone number. Touts at tourist areas will try to mislead you into getting into the wrong car when you leave; if you fall for this you will certainly be ripped off, your car may be stolen and you may be sexually assaulted.
Be wary of reckless driving when renting a car with a driver. Do not be afraid to tell the driver that you have time to see around and that you are not in a hurry. Make sure also that your driver gets enough rest time and time to eat. In general as you visit restaurants, the driver may eat at the same time (either separately at the same restaurant or at some other nearby place). They may be willing to work nonstop for you as you are the "boss", but your life depends on their ability to concentrate, so ensure that your driving demands are reasonable; for example, if you decide to carry your own food with you on the road, be sure to offer your driver time to get a lunch himself.
Avoid travelling at night. Indian roads are dimly lit if at all, and there are even more hazards on the road after dark — even highway bandits if you get far enough off the beaten track.
Self-drive car rental
If you feel confident enough to drive by yourself, you can now hire a self-drive car in many major cities. These cars are available for long-distance as well as intra-city travel. The choices you get may be different from what are available in your home country, and these service providers may not accept international licences. Do your research well before opting for this choice. Some of the options are:
By motorcycle

Some people argue that the best way to experience India is on a motorbike. Riding a motorbike and travelling across India you get a closer look and feel of India along with all the smells and sounds. There are companies which organise package tours or tailor-made tours for enthusiastic bikers and the adventurous, or a safer motorbike experience of India. Blazing Trails tours, Wild Experience tours and Extreme Bike tours are some such companies.
Another choice, popular with people who like taking risks, is to buy a motorcycle. Not for the faint of heart or inexperienced rider. India boasts the highest motor vehicle accident rate in the world.
The Royal Enfield is a popular (some would say, the only) choice for its classic looks and macho mystique. This despite its high petrol consumption, 25 km/litre to 30 km/litre, supposed low reliability (it is "classic" 1940s engineering after all and requires regular service adjustment; you can find an Enfield mechanic who has worked on this bike for ten, twenty, thirty years in every town in India, who will perform miracles at about ₹100 an hour labour cost), and claimed difficulty to handle (actually the bike handles beautifully, but may be a wee heavy and seat high for some).
Or, one can opt for the smaller yet quicker and more fuel efficient bikes. They can range from 100 cc to the newly launched 220 cc bikes. Three most popular bike manufacturers are Hero, Bajaj and Honda. The smaller variants (100-125 cc) can give you a mileage exceeding 50 km/litre on the road, while giving less power if one is opting to drive with pillion on the highways. The bigger variants (150-220 cc) are more powerful and one can get a feel of the power especially on highways - the mileage is lesser for these bikes anywhere between 35 km/litre to 45 km/litre.
Preferably tourists should go for second hand bikes rather than purchasing new ones. The smaller 100 cc variants can be purchased for anywhere between ₹15,000-25,000 depending on the year of make and condition of vehicle. The bigger ones can be brought from ₹30,000 onwards.
By hitch hiking
Hitch-hiking in India is very easy due to the enormous number of cargo trucks on every highway and road. Most drivers do not speak English or any other international language; however, most have a very keen sense of where the cities and villages are along the road. It is rare for any of them to expect payment. For safety concerns, it is not recommended as all the drivers cannot be trusted. Hitch-hiking in cities, highways and crowded places is safe, but refrain from hitchhiking on deserted places, less populated areas, forest roads, etc.
By auto-rickshaw

The auto-rickshaw, usually abbreviated and referred to as auto and sometimes as rickshaw, is the most common means of hired transportation in India. They are very handy for short-distance travel in cities, especially since they can weave their way through small alleys to bypass larger cars stuck in travel jams, but are not very suitable for long distances. Most are green and yellow, due to the new CNG gas laws, and some may be yellow and black in colour, with one wheel in the front and two in the back, with a leather or soft plastic top.
When getting an auto-rickshaw, you can either negotiate the fare or go by the meter. In almost all cases it is better to use the meter—a negotiated fare means that you are being charged a higher than normal rate. A metered fare starts around ₹13(different for different areas), and includes the first 1 to 2 kilometres of travel. Never get in an auto-rickshaw without either the meter being turned on, or the fare negotiated in advance. In nearly all cases the driver will ask an exorbitant sum (for Indian standards) from you later. A normal fare would be ₹11-12 for the first km and ₹7-8 per km after that. In most cities, auto-rickshaw drivers are provided with a rate card that elaborately describes the fares on per kilometre basis. A careful tourist must verify the meter reading against the rate card before making a payment. Auto-rickshaws carry either digital or analog meters wherein the analog meters may have been tampered with. It may be a better option to go for a negotiated fare when the auto-rickshaw has an analogue meter.
Ideally, you should talk with a local to find out what the fare for any estimated route will be. Higher rates may apply at night, and for special destinations such as airports. Finally, factor in that auto drivers may have to pay bribes to join the queue for customers at premium locations such as expensive hotels. The bribe will be factored in the fare.
Make sure that the driver knows where he is going. Many autorickshaw drivers will claim to know the destination without really having any clue as to where it is. If you know something about the location, quiz them on it to screen out the liars. If you do not know much about the location, make them tell you in no uncertain terms that they know where it is. This is because after they get lost and drive all over the place, they will often demand extra payment for their own mistake. You can then tell them that they lied to you, and wasted your time, so they should be happy to get the agreed-upon fee.
Addresses
If you need to get anywhere, call in advance and ask for detailed directions. Bear in mind that street signs in India tend to be rare or nonexistent outside the cities. Postal addresses will often carry landmark details "Opp. Prithvi theatre" or "Behind Maruti Showroom" or "near temple / church / mosque / bank branch / police station / school" to ease the search. Unlike the western system of address, the Indian system uses plot number or house number, street, road followed by landmark and the location pin code instead of street name and block number. Finding a place will usually involve some searching, but you will always find someone around the area willing to guide you. Unlike many other countries, Indians ask passers-by, nearby shopkeepers or cops for guidance on street addresses. So you may do the same, people would be happy to help. Using Google maps with GPS works well most of the time in major cities but at times may not be accurate due to incorrect spelling of road or incorrect positioning on map.
Inner Line permit
Inner Line Permit is an official travel document issued by the Government of India to allow inward travel of an Indian citizen into a protected/restricted area for a limited period. It is obligatory for Indian citizens from outside those states to obtain a permit for entering into the protected state. The document is an effort by the Government to regulate movement to certain areas near the international border of India. This is a security measure and it is applicable for the following states:
- Arunachal Pradesh – permits are issued by the Secretary of the Government of Arunachal Pradesh. The permits are required for entering the Indian state of Arunachal Pradesh through any of the check gates across the inter-state border with Assam or Nagaland. Permits are obtained at Arunachal Bhavan in all major cities. Permits are given to specific districts and therefore plan the itinerary before applying for district entry permits. Checkpoints at every district border only allow locals and permit holders.
- Manipur - permits are issued by the Government of Manipur to allow inward travel of an Indian citizen into the state for a limited period to avoid uncontrollable influx. Foreign tourists are not provided the permits.
- Mizoram – permits are issued by the Government of Mizoram. The permit is required for entering the Indian state of Mizoram through any of the check gates across the inter-state borders.
- Nagaland – a permit is mandatory for a mainland Indian citizen entering the state of Nagaland through any of the check gates across the inter-state borders.
- Sikkim - a permit required for the 'Nathu La' Pass which was an important passage of the silk route in medieval era and now a part of the border between India and China. Foreigners are not provided the permits. Only Indian citizens are allowed beyond the point. Further permits for high altitude regions like 'Lachung-Lachen' along with a high altitude lake called 'Gurudongmar Lake' can be obtained from Gangtok directly. Foreigners may be allowed. Another point known as 'Zero Point' also requires permits.
- Andaman and Nicobar Islands - non-Indians need a Restricted Area Permit to visit the islands, but these are now issued on arrival at the Port Blair airport; if you plan to arrive by sea, you'll need to arrange your permit before arrival, either in Chennai or when applying for your Indian visa. Indian nationals do not require a permit to visit the Andamans, but permits are required to visit Nicobar Islands and other tribal areas, and are rarely given.
See
To see all the places worth visiting in India, even a 6-month visit is arguably inadequate. There are more tourist destinations in India than can be mentioned in a full-length book, let alone a summary. Almost every state in India has over ten major tourist destinations and there are cities which can barely be tasted in a full week. Several Indian states by themselves are bigger and more populous than most of the countries in the world, and there are 29 states and 7 Union Territories in India, including two island chains outside the Mainland.
That said, below are some highlights.
Historical monuments and forts
Probably the most famous single attraction in India is the Taj Mahal, which is widely recognised as the jewel of Islamic art in India and one of the universally admired masterpieces of the world's heritage.

The Qutb Minar and the impressive Red Fort are the two most prominent historical monuments in Delhi.
Jaipur, the capital of the western state of Rajasthan, is incredibly rich in forts and palaces, including the tremendous Amber Fort, beautiful Jal Mahal (Water Palace) and unique Hawa Mahal.
Nalanda in Bihar has the remains of a university of Buddhism that was established in 450 CE.
For a rather different and more modern kind of historical monument, the Gandhi Ashram in Ahmedabad, founded by the Mahatma himself, is a repository of all things Gandhi.
Houses of worship
No visit to India would be complete without a trip to some of the country's fantastic temples. All regions of the country are replete with temples. The city of Jammu, the winter capital of Jammu and Kashmir state, has so many temples that it's called the "City of Temples" and is a major draw for Hindu pilgrims. Bishnupur in West Bengal is home to famous terracotta temples. The Sri Venkateswara Temple in Tirupati, Andhra Pradesh, is dedicated to Vishnu and is also a major draw for pilgrims. The Tantric temple complexes of Khajuraho in Madhya Pradesh are much beloved for their thousand-year-old sacred erotic wall carvings, considered by some art historians to be the pinnacle of erotic art. The Meenakshi Amman Temple in Madurai, Tamil Nadu, is a centre of worship of Parvati, the consort of Shiva. The city of Thanjavur in Tamil Nadu known for its grand Chola-era temples.
Hinduism is not the only religion represented among the great temples of India. The world headquarters of the Sikh religion are in the Golden Temple in Amritsar, Punjab. Leh and environs, in the Kashmiri region of Ladakh, are one of a number of areas that have splendid Buddhist temples or monasteries. The Ranakpur Temple in the small Rajasthani town of Ranakpur is an impressive and historic Jain temple.
India's second-largest religion in adherents after Hinduism is Islam, and many parts of India were ruled by Muslim dynasties for hundreds of years, so it's not surprising that India is also home to many magnificent mosques. Some of them, like the mosque in the Taj, are part of historical monuments. One impressive mosque that's very much in use to this day is the lovely 17th-century Jama Masjid in Old Delhi. Hyderabad in the south has several historical mosques, including Charminar Masjid and Mecca Masjid.
There are also notable churches in various Indian cities, and the dwindling ancient Jewish community of Kochi, Kerala, continues to use their famous synagogue, which is a tourist attraction nowadays.
Geographical

India is a very geographically varied country. In the north of the country, one can see the Himalayas, the Earth's highest mountain range. There are hilly areas in many non-Himalayan states, too. In India, hill stations — towns in the cooler areas in foothills or high valleys surrounded by mountains, which were favored by rajas, then the British and now Indian tourists in the hot summer months — are considered sights and experiences in themselves. The largest of them is Jammu and Kashmir's summer capital, Srinagar, but Darjeeling, in view of Mount Kangchenjunga in the northern part of West Bengal, is very famous for its tea. Other famous hill stations include Shimla, Ooty and Gangtok, and there are many others — most states have some.
India is also a country of numerous rivers. Several of them are traditionally considered holy, but especially the Ganges, locally known as Ganga, which brings life to the Indian Plains, India's breadbasket, and is not just an impressive body of water but a centre of ritual ablutions, prayer and cremation. There are several holy cities along the river that have many temples, but they are often less places of pilgrimage to specific temples than holy cities whose temples have grown because of the ghats (steps leading down to the holy river) and most interesting to visit for the overall experience of observing or partaking in the way of life and death along the river. Foremost among these holy cities is Varanasi, Uttar Pradesh, where some 5,000-year-old rituals are still practised; other cities worth visiting to experience the Ganges include Rishikesh and Haridwar, much further upstream.
India also has a long coastline. The beaches of Goa, also an interesting former Portuguese colony; Kochi; and the Andaman Islands are among the most appreciated by domestic and foreign visitors.
Finally, India has a vast desert, the Thar Desert in Rajasthan. Several Rajasthani cities including Jaisalmer are good bases for camel safaris.
Wildlife
India is famous for its wildlife, including the Bengal tigers, Asiatic lions and elephants.
- Keibul Lamjao National Park in Manipur is the world's only floating national park, floating on the mirror like Loktak lake, where the world's only dancing deer species, Brow antlered deer (Manipuri: Sangai) is found. Another one, the Sirohi National Park is the world's only habitat for the world's only terrestrial lily, the Shirui Lily (Lilium macklineae), which can't be grown in any part of the earth except in the Shirui NP in Manipur, despite innumerable serious experiments of numerous scientists.
- Bandhavgarh National Park in Madhya Pradesh and Ranthambhore National Park in Rajasthan are the most likely places for you to spot an Indian tiger in the wild, though you will still have to have some luck and persistence.
- Gir Forest National Park in Gujarat is dedicated to the preservation of Asiatic lions.
- Sundarbans National Park, on the border with Bangladesh is the largest mangrove forest and delta in the world, home to the famous Royal Bengal tigers and estuarine crocodiles but also fascinating as an overall ecosystem.
- Pench National Park in Madhya Pradesh is one of the places that may have inspired Rudyard Kipling's Jungle Book.
- Kaziranga National Park in Assam is home to the world's largest population of one-horned rhinoceros.
Do
Fairs and festivals
Goa Fair (carnival). February heralds the carnival at Goa. For three days and nights the streets come alive with colour. Held in mid February the week-long event is a time for lively processions, floats, the strumming of guitars, graceful dances and of non-stop festivity. One of the more famous of Indian carnivals, the Goa Festival is a complete sell out in terms of tourism capacities.
Surajkund Mela (1–15 February). As spring glides in, full of warmth and vibrancy, leaving the grey winter behind, Surajkund adorns itself with colourful traditional crafts of India. Craftsmen from all over the country assemble at Surajkund during the first fortnight of February to participate in the annual celebration that is the Surajkund Crafts Mela.
Holi. The Spring Festival of India, Holi is a festival of colours. Celebrated in March or April, according to the Hindu calendar, it was meant to welcome spring and win the blessings of Gods for good harvests and fertility of the land. As with all Hindu festivals, there are many interesting legends attached to Holi, the most popular being that of Prince Prahlad, who was a devout follower of Lord Vishnu. It is the second most important festival of India after Diwali. Holi in India is a festival of fun and frolic and has been associated with the immortal love of Krishna and Radha. The exuberance and the festivity of the season are remarkable.
Diwali. The festival of lights, Diwali, illuminates the darkness of the New Year's moon, and is said to strengthen close friendships and knowledge with a self-realisation. Diwali is celebrated on a nation-wide scale on Amavasya – the 15th day of the dark fortnight of the Hindu month of Ashwin (Oct/Nov) every year. It symbolises that age-old culture of India which teaches to vanquish ignorance that subdues humanity and to drive away darkness that engulfs the light of knowledge. The festival of lights still today projects the rich and glorious past of India.
Pushkar Mela. Every November the sleepy little township of Pushkar in Rajasthan comes alive in a riot of colours and a frenzied burst of activity during the Pushkar Fair. Few fairs in the world can match the liveliness of Pushkar. It includes the world's largest camel fair, but is much more than that.
Sports
- Polo. Polo is a gift from Manipur, India to the world. The game was taken from India by the Europeans during the 19th century and spread across the globe. "Polo can be traced to origins in Manipur state c. 3100 BC, when it was played as Sagol Kangjei." - Guinness World Records, 1991, page no. 706. The Imphal Polo Ground (Manipuri: Mapal Kangjeibung) is the world's oldest polo ground and is in the heart of Imphal, the capital city of Manipur.
- Cricket. India is a cricket-obsessed country and cricket is in the blood of most Indians. India plays an important role in world cricket and has been world champion twice in the ICC Cricket World Cup, in 1983 beating the mighty West Indies in the final, and Sri Lanka in 2011. India also emerged triumphant in the inaugural ICC T20 World Cup in 2007 held in South Africa beating arch-rival Pakistan in a nail-biting final. The popularity of cricket in India is second to no other game, so seeing children playing cricket in parks and alleys with rubber balls and makeshift wickets is very common. Until 2008, Indian cricket was all about the national team playing against other countries in one-day matches or epic five-day Test marathons, but the advent of the Indian Premier League (IPL) has, for better or worse, brought fast-paced, commercialised "Twenty20" cricket to the fore, complete with cheerleaders and massive salaries. In international matches, while Australia typically poses the strongest challenge to Indian supremacy, the most intense rivalry by far is with neighbouring Pakistan, and matches between the two sides are often a very charged affair. About half-a dozen Indian stadiums have a capacity of over 45,000 and watching a cricket match can be quite an experience. Eden Gardens cricket stadium in Kolkata is Asia's highest capacity stadium with a 66,349 seating capacity and is the oldest cricket stadium in the Indian subcontinent, established in 1865, and is comparable to the stadiums of Lords' in London and the MCG in Melbourne. The atmosphere of most matches is electrifying. Nearly all international matches have sellout crowds, and it is quite normal for fans to bribe officials and make their way in. Starting ticket prices are quite cheap; they can be as low as ₹250–300. India and Pakistan are all-time arch rivals, and cricket matches between the two nations attract up to a billion TV viewers, including many people who are otherwise not cricket fans.
- Football. You can come across young boys playing with a football on any open space that is available, as with cricket. Club football is very popular, especially among youth and you will find people getting into heated arguments in public places over their favorite teams. Many people also support national teams other than India, but it usually depends on the nationality of their favourite players. Also, many large restaurants and bars offer a view of important European club matches and the World Cup matches. The most famous and electrifying rivalry is the Kolkata Derby between Mohun Bagan Athletic club (established 1889) and East Bengal Football club (Estd.-1920) held in Salt Lake stadium (the second-largest non-auto racing stadium in the world) in Kolkata, the football capital of India and a tremendously football crazy city. This rivalry is widely regarded to be the oldest and most intense football rivalry in Asia.
- Hockey (field hockey). The national game of India, hockey retains a prominent position in the hearts of many Indians, despite the craze for cricket and football. Although the viewership has dwindled significantly (as compared to the golden era before cricket came to the fore in the mid-1980s), it hasn't vanished completely. It still has a significant fan base, especially in North India, some eastern parts like Jharkhand, Odisha and the Northeastern states. The introduction of the Premier Hockey League has helped restore its popularity.
- Formula One. Not very popular in India, though there has been one Formula One race held at Noida. People now know the names of drivers such as Sebastian Vettel and Fernando Alonso, while ten years earlier only a few knew this sport.
Buy
Money
|
Exchange rates for Indian rupees As of March 2022:
Exchange rates fluctuate. Current rates for these and other currencies are available from XE.com |
|
The money that isn't In 2016, the old yellow ₹500 and red ₹1000 banknotes were demonetised (made invalid) at very short notice in a ham-fisted attempt to fight corruption. If you have any lying around, they are no longer legal tender and they're impossible to exchange, so don't accept these if somebody tries to palm any off to you: The new ₹500 note is brown, and there is no ₹1000 note at all. The new ₹2000 note is magenta in colour. |
The currency in India is the Indian rupee (sign: ₹; code: INR) (रुपया — rupaya in Hindi and similarly named in most Indian languages, but taka in Maithili, Taakaa in Bengali and Toka in Assamese). The rupee is subdivided into 100 paise (singular: paisa). "5 rupees 75 paise" would normally be written as "₹5.75". The new rupee symbol ₹ was introduced in July 2010 to bring the rupee's symbol in line with other major currencies. Previously, "Rs" was used (or "Re" for the singular rupee). It is very likely you will continue to see the previous nomenclature in your Indian travels, especially with smaller businesses and street vendors.
Indian banknotes or bills come in denominations of ₹5 (green) [printing discontinued], ₹10 (orange and violet/chocolate brown), ₹20 (reddish-orange/greenish yellow), ₹50 (violet/fluorescent blue), ₹100 (greenish blue/lavender), ₹200 (bright yellow), ₹500 (stone grey) and ₹2,000 (magenta). There are two versions of ₹10, ₹20, ₹50 and ₹100 banknotes due to the introduction of a new series of the currency by the government in 2016 following the demonetisation. It is always good to have a number of small bills on hand, as merchants and drivers sometimes have no change. A useful technique is to keep small bills (₹10-50) in your wallet or in a pocket, and to keep larger bills separate. Then, it will not be obvious how much money you have. Many merchants will claim that they don't have change for a ₹100 or ₹500 note. This is often a lie so that they are not stuck with a large bill. It is best not to buy unless you have exact change.
The coins in circulation are ₹1, ₹2, ₹5, and ₹10. Coins are useful for buying tea (₹5), for bus fares (₹2 to ₹10), and for giving exact change for an auto-rickshaw.
Indians commonly use lakh and crore for 100,000 and 10,000,000 respectively. Though these terms come from Sanskrit, they have been adopted so deeply into Indian English that most people are not aware that they are non-existent in other English dialects. You may also find non-standard, although standard in India, placement of commas while writing numerals. One crore rupees would be written as ₹1,00,00,000, so first time you place a comma after three numerals, then after every two numerals. This format may puzzle you till you start thinking in terms of lakhs and crores, after which it will seem natural.
| Number | English Format | Indian Format (In English) | Indian Format (In Hindi) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 100 | Hundred | Hundred | Sau |
| 1000 | Thousand | Thousand | Hazaar |
| 1,00,000 | Hundred Thousand | One Lakh | Ek Lakh |
| 10,00,000 | Million | Ten Lakhs | Das Lakh |
| 1,00,00,000 | Ten Million | One Crore | Ek Crore |
Converting from rupees to dollars, euros and pounds
Your usual currency equalling between 58 and 80 rupees, do this to convert a price in rupees: Divide by 100 and add the half of it. Example:
• ₹800 / 100 = 8; 8 + 4 ≈ 12 of your usual currency
When your usual currency equals between 80 and 110 rupees, do this to convert a price in rupees: Divide by 100. Example:
• ₹900 / 100 ≈ 9 of your usual currency
And your usual currency being between 110 and 133 rupees, do this to convert a price in rupees: Divide by 1000 and multiply by 8. Example:
• ₹1000 / 1000 = 1; 1 * 8 ≈ 8 of your usual currency
This works well for everyday expenses. For rather high amounts of money, it's better to convert with the exact exchange rate, e.g. with an app.
Changing money

The Indian rupee is not fully convertible; foreigners are not allowed to bring Indian rupees into or out of India, while Indian citizens are restricted to carrying up to ₹25,000 when exiting or entering India. Rates for exchanging rupees overseas are often poor, although places with significant Indian populations (e.g. Dubai, Singapore) can give decent rates.
You can change foreign currencies into rupees at any one of the numerous foreign exchange conversion units including banks. Most ATMs will pay out ₹10,000 in each transaction. State Bank of India (SBI) is the biggest bank in India and has the most ATMs. ICICI bank has the second largest network of ATMs and accepts most of the international cards at a nominal charge. International banks like Citibank, HSBC, Barclays, Deutsche Bank, ABN Amro and Standard Chartered have a significant presence in major Indian cities. It is always worthwhile to have bank cards or credit cards from at least two different providers to ensure that you have a backup available in case one card is suspended by your bank or simply does not work work at a particular ATM.
In many cities and towns, credit cards are accepted at retail chain stores and other restaurants and stores. Small businesses and family-run stores almost never accept credit cards, so it is useful to keep a moderate amount of cash on hand.
Electronic payments including Google Pay, PayPe and Paytm are increasingly popular across India, but you will need both an Indian phone number and an Indian bank account to sign up.
Maximum Retail Price - MRP
When buying factory packaged food or drinks (e.g. lemonade, cola, etc.) always have a look for a stamp on the packaging. It will tell you the MRP (short for maximum retail price) and you can't be forced to pay more than that.
Costs
Costs in India can vary widely from region to region, and even in the same city, depending on the quality of service or product, brand, etc. But usually, India is not very expensive for the foreign traveller.
Mid-range to high-range travellers
₹ 5000, at least, needed for a decent room in a good hotel offering cable TV, air conditioning and a direct telephone; however, this price doesn't include a refrigerator. Food will cost at least ₹150 for a decent meal (at a stall, not a hotel), but the sky is the limit. While bus transportation will cost approximately ₹5 for a short distance of about 1 km, a taxi or rickshaw may cost ₹20-₹30 for the same distance without air conditioning. There are radio taxis that are available at ₹ 20 to 25 per km in key Indian cities which have GPS navigation, air conditioned and accept debit/credit cards for payments. They are a very safe mode of travel. So the total for one day would be about as below:
- Hotel: US$60 for a good place per day
- Food: US$10 for a good meal per day
- Travel: US$10 taxi and bus together
Total: US$80 for a couple, US$70 for a person alone
Budget travellers
Budget travel around India is surprisingly easy, with the savvy backpacker able to get by (relatively comfortably) on as little as US$25–35 per day. It is generally cheaper than South East Asia with a night in a hotel costing as little as ₹200-1,000 (though there will be probably no air conditioning or room service for this price). Beach huts in the cheaper places of Goa can cost around ₹800 per night. A meal can be bought from a street trader for as little as ₹30, though, in a restaurant expect, to pay around ₹200-300 for a beer or two. Overnight buses and trains can cost anywhere from ₹600-1,000 dependent on distance and locations, though an uncomfortable government bus (benches only) may be cheaper.
Tipping
In India there has traditionally been little or no tipping, and today tipping is unusual outside of fancier restaurants where up to 10% is appropriate. The fancier restaurants may also levy a service charge of up to 15% apart from government taxes. Some restaurants have also have started placing jars at the cashier for people to drop in some change if they feel so, but this is a rather rare phenomenon. Most clubs in India have a complete ban on its members from tipping. Usually no service industry except the food services industry expects a tip. In India, it is unlawful for taxi or rickshaw drivers to charge anything above the meter.
Shopping

In India, you are expected to negotiate the price with street hawkers but not in department stores and the like. If not, you risk overpaying many times, which can be okay if you think that it is cheaper than at home. In most of the big cities and even smaller towns retail chain stores are popping up where the shopping experience is essentially identical to similar stores in the West. There are also some government-run stores like the Cottage Emporium in New Delhi, where you can sample wares from all across the country in air-conditioned comfort. Although you will pay a little more at these stores, you can be sure that what you are getting is not a cheap knockoff. The harder you bargain, the more you save money. A few tries later, you will realise that it is fun.
Often, the more time you spend in a shop, the better deals you will get. It is worth spending time getting to know the owner, asking questions, and getting him to show you other products (if you are interested). Once the owner feels that they will make a sufficient profit from you, they will often give you additional goods at a rate close to cost, rather than the common "foreigner rate". You will get better prices and service by buying many items in one store than by bargaining in multiple stores individually. If you see local people buying in a store, you should be able to find out the real Indian prices. Ask someone around you quietly, "How much would you pay for this?"
Also, very often you will meet a "friend" in the street inviting you to visit their family's shop. That almost always means that you pay twice as much as when you had been in the shop without your newly found friend.
Baksheesh was originally a Persian word for charity, but it has spread to many languages including most of those in India. Depending on context, its English translation might be any of donation, gift, tip, bribe, alms or commission. Having Indians you deal with want baksheesh is a fairly common phenomenon. While this is sometimes a problem, doing it can ease certain problems and clear some hurdles. Baksheesh is also the term used by beggars when they want money from you and may refer to tips given those who provide you a service.
Packaged goods show the Maximum Retail Price (MRP) on the package. This includes taxes. Retailers are not supposed to charge more than this. Though this rule is adhered to at most places, at tourist destinations or remote places, you may be charged more. This is especially true for cold drinks like Coke or Pepsi, where a bottle (300 ml) costs around ₹33-35 when the actual price is ₹30. Also, keep in mind that a surprising number of things do not come in packaged form. Do check for the authenticity of the MRP, as shopkeepers may put up their own sticker to charge more from you.
What to look for/buy
- Wood Carvings: India produces a striking variety of carved wood products that can be bought at very low prices. Examples include decorative wooden plates, bowls, artwork, furniture and miscellaneous items that will surprise you. Check the regulations of your home country before attempting to import wooden items.
- Clothing: It depends on the state/region you are visiting. Most of the states have their speciality to offer. For example go for silk sarees if you are visiting Benaras; Block prints if you are in Jaipur
- Paintings: Paintings come on a wide variety of media, such as cotton, silk, or with frame included. Gemstone paintings incorporate semi-precious stone dust, so they have a glittering appearance to them.
- Marble and stone carvings: Common carved items include elephants, Hindu gods/goddesses. Compare several of the same kind. If they look too similar bargain hard as they are probably machine made.
- Jewellery: Beautiful necklaces, bracelets and other jewellery are very inexpensive in India.
- Pillow covers, bedsets: Striking and rich designs are common for pillows and bed covers.
- Carpets: India has a long history of carpet production and makes many today for both domestic and export markets.
Designer brands like Louis Vuitton, Prada, Gucci, Zara, A & F, all are available in upmarket stores.
Eat
- See also: South Asian cuisine
Indian cuisine takes its place among the great cuisines of the world. There is a good chance that you'd have tasted "Indian food" in your country, especially if you are a traveller from the West, but what India has exported abroad is just one part of its extraordinary range of culinary diversity.
Indian food can be spicy: Potent fresh green chilis or red chili powder will bring tears to the eyes of the uninitiated, and can be found in unexpected places like sweet cornflakes (a snack, not breakfast) or even candies. The degree of spiciness varies widely throughout the country: Andhra food is famously fiery, while Gujarati cuisine is quite mild in taste with the exception of Surti food (from Surat).
To enjoy the local food, start slowly. Don't try everything at once. After a few weeks, you can get accustomed to spicy food. If you would like to order your dish not spicy, simply say so. Most visitors are tempted to try at least some of the spicy concoctions, and most discover that the sting is worth the trouble. Remember, too, that while "spicy" is a convenient short-hand for "chili-laden," the spiciness of food in India doesn't always mean lots of chili: Indian cuisines often use a multitude of different spices and other aromatic ingredients in highly creative and flavourful ways.
Cuisine
Cuisine in India varies greatly from region to region. The "Indian food" served by many so-called Indian restaurants in the Western hemisphere is inspired by North Indian cooking, specifically Mughlai cuisine, a style developed by the royal kitchens of the historical Mughal Empire, and the regional cuisine of the Punjab, although it has been Britainised and the degree of authenticity in relation to actual Mughlai or Punjabi cooking is variable at best and dubious at worst.

North India is a wheat-growing area, so you have Indian breads (known as roti), including chapatti (unleavened bread), paratha (pan-fried layered roti), naan (cooked in a clay tandoor oven), puri (deep-fried and puffed up bread) and many more. A typical meal consists of one or more gravy dishes along with rotis, to be eaten by breaking off a piece of roti, dipping it in the gravy and eating them together. Most of the Hindi heartland of India survives on roti, rice, and lentils (dal), which are prepared in several different ways and made spicy to taste. Served on the side, you will usually find spiced yogurt (raita) and either fresh chutney or a tiny piece of exceedingly pungent pickle (achar), very much an acquired taste for most visitors — try mixing it with curry, not eating it plain.
A variety of regional cuisines can be found throughout the North. Tandoori chicken, prepared in a clay oven called a tandoor, is probably the best-known North Indian dish, innovated by a Punjabi immigrant from present-day Pakistan during the Partition. For a taste of traditional Punjabi folk cooking, try dal makhani (stewed black lentils and kidney beans in a buttery gravy), or sarson da saag, a yummy gravy dish made with stewed mustard greens, served with makke di roti (flatbread made from maize). There are also the hearty textures and robust flavours of Rajasthani food, the meat-heavy Kashmiri dishes from the valley of Kashmir, or the mild yet ingratiating Himalayan (pahari) cuisine found in the higher reaches. North India also has of a variety of snacks like samosa (vegetables encased in thin pastry of a triangular shape) and kachori (either vegetable or pulses encased in thin pastry). There is also a vast constellation of sweet desserts like jalebi (deep-fried pretzel with sugar syrup- shaped like a spiral), rasmalai (balls of curds soaked in condensed milk) and halwa. Dry fruits and nuts like almonds, cashews and pistachios are used a lot, often in the desserts, but sometimes also in the main meal.
Authentic Mughal-style cooking, the royal cuisine of the Mughal Empire, can still be found and savoured in some parts of India, most notably the old Mughal cities of Delhi, Agra and Lucknow in Uttar Pradesh, and Hyderabad in Telangana. It is a refined blend of Persian, Turkic and Subcontinent cooking, and makes heavy use of meat and spices. The names of some Mughal dishes bear the prefix of shahi as a sign of its prestige and royal status from a bygone era. Famous Mughal specialties include biryani (layered meat and rice casserole), pulao (rice cooked in a meat or vegetable broth), kebab (grilled meat), kofta (balls of mincemeat), rumali roti (flatbread whirled into paper-thin consistency) and shahi tukray (saffron and cardamom-scented bread pudding).

- See also: Southern India#Eat
In South India, the food is mostly rice-based. A typical meal includes sambhar (a thick vegetable and lentil chowder) with rice, rasam (a thin, peppery soup), or avial (mixed vegetables) with rice, traditionally served on a banana leaf as a plate. Seasoning in South India differs from northern regions by its ubiquitous use of mustard seeds, curry leaves, pulses, fenugreek seeds, and a variety of souring agents such as tamarind and kokum. There are regional variations too — the coastal regions make greater use of coconut and fish. In the State of Kerala, it is common to use grated coconut in everything and coconut oil for cooking, while someone from the interior could be surprised to learn that coconut oil can be used for cooking. The South also has some great breakfast dishes like idli (a steamed cake of lentils and rice), dosa, a thin, crispy pancake often stuffed with spiced potatoes to make masala dosa, vada, a savoury Indian donut, and uttapam, a fried pancake made from a rice and lentil batter with onions and other vegetables mixed in. All of these can be eaten with dahi, plain yogurt, and chutney, a condiment that can be made from practically anything. Try the ever popular masala dosa, which originated from Udupi in Karnataka, in one of the old restaurants of Bangalore like CTR and Janatha in Malleswaram or Vidyarthi Bhavan in Basavangudi or at MTR near Lalbagh. South Indian cuisine is predominantly vegetarian, though there are exceptions: Seafood is very popular in Kerala and the Mangalorean coast of Karnataka; and Chettinad and Hyderabad cuisines use meat heavily, and are a lot spicier. Coffee tends to be the preferred drink to tea in South India.
To the West, you will find some great cuisine groups. Gujarati cuisine is somewhat similar to Rajastani cooking with the heavy use of dairy products, but differs in that it is predominantly vegetarian, and often sweetened with jaggery or sugar. Gujaratis make some of the best snack items such as the Dhokla and the Muthia. Mumbai is famous for its chaat, as well as the food of the small but visible Irani and Parsi communities concentrated in and around the city. The adjacent states of Maharashtra and Goa are renowned for their seafood, often simply grilled, fried or poached in coconut milk. A notable feature of Goan cooking is that pork and vinegar is used, a rare sight in the rest of India. Vindaloo originated in Goa, and is traditionally cooked with pork, and in spite of its apparent popularity in Indian restaurants abroad, it is not common in India itself.

To the East, Bengali and Odishan food makes heavy use of rice, and fish due to the vast river channels and ocean coastline in the region. Bengali cooking is known for its complexity of flavor and bittersweet balance. Mustard oil, derived from mustard seeds, is often used in cooking and adds a pungent, slightly sweet flavour and intense heat. Bengalis prefer freshwater fish, in particular the iconic ilish or hilsa: it can be smoked, fried, steamed, baked in young plantain leaves, cooked with curd, aubergine and cumin seeds. It is said that ilish can be prepared in more than 50 ways. Typical Bengali dishes include maccher jhal, a brothy fish stew which literally means "fish in sauce", and shorshe ilish (cooked in a gravy made from mustard seed paste). Eastern India is also famous for its desserts and sweets: Rasgulla is a famous variant of the better-known gulab jamun, a spherical morsel made from cow's milk and soaked in a clear sugar syrup. It's excellent if consumed fresh or within a day after it is made. Sondesh is another excellent milk-based sweet, best described as the dry equivalent of ras malai.
A lot of food has also filtered in from other countries. Indian Chinese (or Chindian) is far and away the most common adaptation: most Chinese would barely recognise the stuff, but dishes like veg manchurian (deep-fried vegetable balls in a chilli-soy-ginger sauce) and chilli chicken are very much a part of the Indian cultural landscape and worth a try. The British left fish and chips and some fusion dishes like mulligatawny soup, while Tibetan and Nepali food, especially momo dumplings, are not uncommon in north India. Pizza has entered India in a big way, and the chains such as Pizza Hut and Domino's have Indianised the pizza and introduced adaptations like paneer-tikka pizza. There is an Indian chain called Smokin Joe's, based in Mumbai, which has mixed Thai curry with pizzas.
It is, of course, impossible to do full justice to the range and diversity of Indian food in this brief section. Not only does every region of India have a distinctive cuisine, but you will also find that even within a region, castes and ethnic communities have different styles of cooking and often have their signature recipes which you will probably not find in restaurants. The adventurous traveller is advised to wangle invitations to homes, try various bylanes of the city and look for food in unlikely places like temples and Gurudhwaras in search of culinary nirvana.
Fruits
While a wide variety of fruits are native to India, including the chikoo and the jackfruit, nothing is closer to an Indian's heart than a juicy ripe mango. Hundreds of varieties are found across most of its regions — in fact, India is the largest producer, growing more than half the world's output. Mangoes are in season at the hottest part of the year, usually between May and July, and range from small (as big as a fist) to some as big as a small cantaloupe. They can be consumed in their ripe, unripe and also a baby form (the last 2 predominantly in pickles). The best mango (the "King of Mangoes", as Indians call it) is the "Alphonso" or Haapoos (in Marathi), in season in April and May along the western coast of Maharashtra. Buy it from a good fruit shop in Mumbai or Mahatma Phule market (formerly Crawford market) in South Mumbai. Dushheri Mangoes are also popular in North India. Other fruits widely available (depending on the season) are bananas, oranges, guavas, lychees, apples, pineapples, pomegranates, apricots, melons, coconuts, grapes, plums, peaches and berries.
Vegetarian
Visiting vegetarians will discover a culinary treasure that is found nowhere else in the world. Owing to a large number of strictly vegetarian Hindus and Jains, Indian cuisine has evolved an astonishingly rich menu that uses no meat or eggs. The Jains in particular practise a strict form of vegetarianism based on the principles of non-violence and peaceful co-operative co-existence: Jains usually do not consume root vegetables such as potatoes, garlic, onions, carrots, radishes, cassava, sweet potatoes and turnips, as the plant needs to be killed prior to its end of normal life cycle, in the process of accessing these . At least half the menus of most restaurants are devoted to vegetarian dishes, and by law all packaged food products in India are tagged with a green dot (vegetarian) or red dot (non-veg). Veganism however is not a well-understood concept in India, and vegans may face a tougher time: milk products like cheese (paneer), yogurt (dahi) and clarified butter (ghee) are used extensively (in particular, ghee can be hard to spot as it can be mixed into curries before they are served), and honey is also commonly used as a sweetener. Milk in India is generally not pasteurised, and must be boiled before consumption.
Even non-vegetarians will soon note that due to the Hindu taboo, beef is generally not served (except in the Muslim and Parsi communities, Goa, Kerala and the North-Eastern states), and pork is also uncommon due to the Muslim population. Chicken and mutton are thus by far the most common meats used, although "buff" (water buffalo) is occasionally served in backpacker establishments. Seafood is of course ubiquitous in the coastal regions of India, and a few regional cuisines do use duck, venison and other game meats in traditional dishes.
Etiquette
In India eating with your hand (instead of cutlery like forks and spoons) is very common. There's one basic rule of etiquette to observe, particularly in non-urban India: Use only your right hand. The left hand is reserved for unhygienic uses. Don't stick either hand into communal serving dishes: instead, use the spatula with your left hand to serve yourself and then dig in.
For all types of breads, the basic technique is to hold down the item with your forefinger and use your middle-finger and thumb to tear off pieces. The pieces can then be dipped in sauce, curry or used to pick up bits before you stuff them in your mouth. Rice is more challenging, but the basic idea is to use four fingers to mix the rice in curry and pack a little ball, before you pop it in your mouth by pushing it with your thumb.
Most of the restaurants do provide cutlery and its pretty safe to use them instead of your hand.
Eating by hand is frowned on in some "classier" places. If you are provided with cutlery and nobody else around you seems to be doing it, then take the hint.
Restaurants
Indian restaurants run the gamut from roadside shacks (dhabas) to classy five-star places where the experience is comparable to places anywhere in the world. Away from the big cities and tourist haunts, mid-level restaurants are scarce, and food choices will be limited to the local cuisine, Punjabi/Mughlai, "Chinese"/"Indo-Chinese" and occasionally South Indian.
|
Menus in English... well, almost Menus in Indian restaurants are usually written in English — but using Hindi names. Here's a quick decoder key that goes a long way for understanding common dishes like aloo gobi and muttar paneer.
|
The credit for popularizing Punjabi cuisine all over the country goes to the dhabas that line India's highways. Their patrons are usually the truckers, who happen to be overwhelmingly Punjabi. The authentic dhaba serves up simple yet tasty seasonal dishes like roti and dal with onions. Hygiene can be an issue in many dhabas, so if one's not up to your standards try another. In rural areas, dhabas are usually the only option.
In South India, a "hotel" is local restaurant serving south Indian food, usually a thali or plate meal—a full plate of food that usually includes a kind of bread and/or rice and an assortment of meat or vegetarian dishes—and prepared meals.
Although you may be handed an extensive menu, most dishes are served only during specific hours, if at all.
Drink
One of the sweetest and safest beverages you can get is tender coconut water (nariyal paani). You can almost always find it in any beach or other tourist destinations in the south. In summer (Mar-Jul), you can get fresh sugarcane juice in many places and even a lot of fresh fruit juice varieties.
India is famous for its Alphonso variety of mangoes, generally regarded as the King of Mangoes among connoisseurs. Frooti, in its famous tetra-pack, is the most popular processed drink, followed by Maaza (bottled by Coca-Cola) or Slice (bottled by PepsiCo), both of which contain about 15% Alphonso mango pulp. Both cost about ₹30-50 for a 600 ml bottle.
As for bottled water, make sure that the cap's seal has not been broken; otherwise, it is a tell-tale sign of tampering or that unscrupulous vendors reuse old bottles and fill them with tap water, which is generally unsafe for foreign tourists to drink without prior boiling. Bottled water brands like Aquafina (by PepsiCo) and Kinley (by Coca-Cola) are widely available. Local brands like Bisleri, being the most popular one is perfectly safe. Tastes may vary due to the individual brands' mineral contents. In semi-urban or rural areas, it may be appropriate to ask for boiled water as well.
Tea

One can get tea (chai in most North Indian languages) of one variety or the other everywhere in India. The most common method of preparing chai is by brewing tea leaves, milk, and sugar altogether in a pot and keeping it hot until it's all sold. It is sweet and uniquely refreshing once you get the taste for it.
Masala chai will have, added to the above mix, spices such as cardamom, ginger or cinnamon etc. For some people, that takes some getting used to.
While Masala chai is popular in Northern and Central India, people in Eastern India (West Bengal and Assam) generally consume tea without spices, the English way. This is also the part of India where most tea is grown.
Coffee
In South India, filter coffee replaces tea as the standard beverage. Indian filter coffee is a coffee drink made by mixing frothed and boiled milk with the decoction obtained by brewing finely ground coffee powder in a traditional Indian filter.
Alcohol

Drinking alcohol can either be frowned upon or openly accepted, depending on the region and religion of the area within which you are drinking. For example, Goa, Punjab and Pondicherry tend to be more free-wheeling (and have low taxes on alcohol), while a few southern areas like Chennai are less tolerant of alcohol, and may even charge excessive taxes on it. Some states such as Gujarat and Bihar are legally "dry" states and alcohol cannot be bought openly there, although there is a substantial bootlegging industry. Bootleg alcohol is unregulated and could kill you or make you sick, and you could also be in legal trouble if you are caught while drunk in a dry state.
Favourite Indian tipples include beer, notably the ubiquitous Kingfisher (a decent lager), and rum, particularly Old Monk. Prices vary by state, especially for hard liquor, but you can expect to pay ₹50-100 for a large bottle of beer and anywhere between ₹170-250 for a 750 ml bottle of Old Monk. Mumbai tends to be the most expensive, due to local taxes, which can be three-times as much as Meghalaya.
Indian wines, long a bit of a joke, have improved remarkably and there's a booming wine industry in the hills of Maharashtra. The good stuff is not particularly cheap (expect to pay around ₹500 a bottle) and selections are mostly limited to white wines, but look out for labels by Chateau Indage[dead link] or Sula.
Illegal moonshine, called tharra when made from sugar cane and toddy when made from coconuts, is widely available in some states. It's cheap and strong, but very dangerous as it may contain poisonous methanol. Quality control is nonexistent, and best avoided entirely. In the former Portuguese colony of Goa you can obtain an extremely pungent liquor called fenny or feni, typically made from cashew fruits or coconuts.
As of April 2017 it is illegal to sell alcohol within 500 m of a highway. This is controversial as it has hit restaurants, bars and hotels hard so check latest rulings before booking your hotel for any changers.
Cannabis

Cannabis in its many forms, especially ganja (weed) and charas (hash), is widely available throughout India, but are all illegal in the vast majority of the country. The law states that simple possession may mean fines or years in prison, depending on the quantity possessed.
However, in some states (notably Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Uttarakhand and Orissa) the one legal and socially accepted way to consume cannabis is as bhang, a low-grade preparation sold at government-licensed shops that is not only smoked, but also made into cookies, chocolate and the infamous bhang lassi, an herb-laced version of the normally innocuous yogurt drink. Bhang lassi is usually available at varying strengths, so use caution if opting for the stronger versions. It's also occasionally sold as "special lassi", but is usually easily spotted by the ₹30-50 price tag (several times higher than the non-special kinds). An important point to bear in mind is that the effects of "Bhang" are slow and heighten when consumed with something sweet. Also, first-time users may want to wait a while before consuming too much in an effort to judge their tolerance.
Sleep
Make sure to bring the passport wherever you go, as most hotels will not rent out rooms without a valid passport. Two important factors to keep in mind when choosing a place to stay are safety and cleanliness. Malaria is present in most areas of India. One way to combat malaria is to choose lodgings with air conditioning and sealed windows. An insect-repellent spray containing DEET will also help, or consider Permethrin-treated fabrics.
Overcharging of foreigners is widespread and you will have to bargain hard. Many hotels listed on western booking websites (booking.com etc.) are also set at the "tourist price"; try local booking sites like Goibibo, redBus or OYO rooms, as these have much better coverage of local hotels and in rural areas.
Choices vary widely depending on budget and location. Good budget hotels in India are easy to find. Cheap travellers' hotels are numerous in big cities where rooms are available for less than ₹450. Rooms at guest-houses with a double bed (and often a bathroom) can be found in many touristic venues for ₹150-200. accommodation in clean dormitories for as little as ₹50 is also available. Bed and breakfast service providers are coming up offering standard services that can be expected from B&Bs outside India. The basics include: air-conditioner or air cooler, free food, and free wi-fi internet.
Most Indian train stations have rooms or dormitories, just ask the railway officials or book it online on the railway's dormitory website. They are cheap, relatively well maintained (the beds, sheets, not the showers), in demand and secure. There are also the added bonus of not being accosted by the rickshaw mafia, getting the bags off quickly and, for the adventurous, high likelihood to jump on a cheap public bus back to the train station. Keep in mind you must have an arrival or departure train ticket from the station where you intend to sleep and there could be a limit on how many nights you may stay.
Midrange options are plentiful in the larger cities and expanding fast into second-tier cities as well. Dependable local chains include Treebo, Country Inns, Ginger and Neemrana, and prices vary from ₹1,000-4,000 per night. Local, unbranded hotels can be found in any city, but quality varies widely.

If the wallet allows it, you can try staying like royalty in a maharaja's palace in places like Udaipur or modern five-star hotels which are now found pretty much all over the country. The top-end of Indian luxury rests with hotel chains like Oberoi, Taj, The Leela and ITC Welcomgroup, who operate hotels in all the major cities and throughout Rajasthan. The usual international chains also run major 5-star hotels in most Indian metropolises, but due to India's economic boom availability is tight and prices can be crazy: it's not uncommon to be quoted over US$300/night for what would in other countries be a distinctly ordinary business hotel going for a third of the price. Also beware that some jurisdictions including Delhi and Bangalore charge stiff luxury taxes on the rack rate of the room, which can lead to nasty surprises at check-out time.
One way of meeting interesting Indian travellers is by staying at an Dak bungalow. Also, called travellers' bungalows or inspection bungalows, they were built by the British to accommodate travelling officials and are now used by the Central and state governments for the same purpose. They exist in many towns and some rural locations. Most will take tourists at a moderate fee if they have room. They are clean, comfortable and usually in good locations, but plain with ceiling fans rather than air conditioning, shower but no bath. Typically the staff includes a pensioned-off soldier as night watchman and perhaps another as gardener; often the gardens are lovely. Sometimes there may be a cook; his or her services will be free but you should buy ingredients.
Reliable electricity supply is present mainly in upmarket hotels. Brownouts are frequent, and many buildings have unsafe wiring. If you like having a beer at the bar or expect alcohol in the room fridge then make sure the hotel is more than 500 m (1,600 ft) from a highway.
Learn
There are many things to learn that interest foreigners all over India, but there are a few destinations that have become particularly well known for certain things:
- Yoga is popular in Haridwar, Rishikesh and Mysore.
- Ayurveda is popular in Kerala. The region also boasts of many dance and dramatic forms.
- Hindi in Delhi and Varanasi.
- Classical musical instruments in not only the ancient city of Varanasi but many parts of India, especially in Southern States, where they form the most integral part of Core Classicals.
- Classical vocal music and classical dance forms in Tamil Nadu or Manipur or Karnataka.
- Sanskrit at 'Samskrita Bharati' in areas of Udupi, Bangalore in the state of Karnataka and Delhi.
- Buddhism in Dharamsala and Bir in Himachal Pradesh as well as in Bodh Gaya in Bihar.
- Cooking classes are also popular. The most well-known exported type of Indian food are the cuisines such as Idly, Dosa, Biryanis, Dals etc and regional cuisines such as Thalis, South Indian, and Punjabi, as the Sikhs have been the most successful in spreading Indian restaurants throughout the western world. However, styles vary a lot throughout the country, so if you have the time and appetite it's worth checking out courses in a variety of areas such as Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and West Bengal.
There are many Universities imparting education but at the helm are Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs) for technical undergraduates, Indian Institutes of Management (IIMs) for management postgraduates and National Law Universities/Schools (NLUs) which are world class institutes. Most of the ambitious students who want to get a good high level education strive to get into these institutes through admission processes which are rather very difficult ones both due to nature of test and the prevailing competition. For example, the 6 top IIMs (Including the 4 oldest - Ahmedabad, Kolkata, Bangalore & Lucknow plus newly established Indore and Kozhikode) together select only about 1,200 students from 350,000 students who appear for CAT exam. But still students have a great desire to get into these institutes. These institutes also offer degrees to foreign students.
Apart from undergraduate, postgraduate and doctoral courses, there are many training and diploma-level institutes and polytechnics that cater to the growing demand for skill-based and vocational education. Besides conventional educational institutes, foreigners might also be interested to study with Pandits to learn Hindi and Sanskrit in genuine settings as well as with Mullahs to study Urdu, Persian, and Arabic. They might also like to live with famed Ustads to study traditional Indian music. Whether people are interested in philosophy or religion, cuisine or dance, India will have the right opportunity for them.
Work
Foreigners need a work permit to be employed in India. A work permit is granted if an application is made to the local Indian embassy along with proof of potential employment and supporting documents. There are many expatriates working in India, mostly for multinational companies. India has always had an expatriate community of reasonable size, and there are many avenues for finding employment, including popular job-hunting websites.
Citizens of Nepal and Bhutan can live and work freely in India, and do not require work permits.
There are many volunteer opportunities around the country including teaching. India has a reasonable presence of foreign Christian missionaries, who for the most part form the non-local religious workers, since the other major religions of the world either grew out of India or have had a long-term presence.
A living can be made in the traveller scenes by providing some kind of service such as baking Western cakes, tattooing or massage.
Previously, an AIDS test result was required as part of the work visa application process. It is highly recommended that applicants obtain test results in their home country beforehand if at all possible.
Stay safe

As a rule India is quite safe for foreigners, apart from instances of petty crime and theft common to any developing country, as long as certain basic precautions and common sense are observed (i.e. women should be cautious travelling alone at night). You can check with your embassy or ask for local advice before heading to Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh in northern-most India, and to Northeast India, i.e. (Assam, Nagaland, Tripura, Mizoram, Meghalaya, Manipur and Arunachal Pradesh). These areas have had serious law and order problems for a long time, though the situation has improved a lot. The same applies while travelling to what used to be a thickly forested area in East-Central India, which covers the states of Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, the eastern edge of Maharashtra and the northern tip of Telangana. Though the problem is only in the remote areas of these states and normal areas to visit in Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Maharashtra or Telangana are safe.
Unfortunately theft is quite common in places visited by tourists, but violent thefts hardly ever occur. More likely a thief will pick your pocket (see pickpockets) or break into your room. So it is better to take precautions to firmly lock the door while indoors, and be on guard while outside.
Some people handling your cash will try to shortchange you or rip you off. In Delhi particularly, this is a universal rule adhered to by all who handle westerners' cash. This does not exclude official ticket sellers at tourist sites, employees at prepaid taxi stands, or merchants in all but the most upscale businesses. Count your cash before handing it over, and be insistent on receiving the correct change.
It is advisable or better to agree on the fare before getting inside an auto or a taxi. This avoids any further unpleasant fare-related arguments. If you can take the advice of a local friend or someone manning your hotel's front desk to know how much it should cost to travel in between two destinations, you will be a smart traveller.
Overseas visitors are often magnets for beggars, frauds and touts. Beggars will often go as far as touching you and following you, tugging on your sleeve. It does little good to get angry or to say "No" loudly. The best response is to look unconcerned and ignore the behaviour. The more attention you pay to a beggar or a tout, positive or negative, the longer they will follow you hoping for a donation. Begging is criminalised in cities such as Mumbai and Delhi. It is however common in many cities, and in pilgrim cities there are sadhus who live an ascetic lifestyle of the seeker that requires them to adopt bhiksha-charya (begging vows) only for sustaining the body.
While hospitality is important in India, it is not common to see people offering to share food or cookies while they eat. Some such offers are genuine and some not. In case you are travelling in train, you are offered food from a big and rich family type group, you can take a bite. But if you are offered something by men or even a couple eating a part of it, try avoiding it, as the other part may have sedatives (this may be so that they may loot your belongings when you become unconscious). You can reply with politeness and say no with a smile; they won't mind or take it personally.
While travelling in public transport (trains, buses) do not accept any food or drink from any local fellow passenger even they are very friendly or polite. There have been instances in which very friendly fellow passengers offered food or drinks including tea or coffee that contained substances that put the victim to sleep whilst all their possessions, including even their clothing, were stolen.
Visitors should not trust strangers offering assistance or services; see Common scams. Be particularly wary of frauds at tourist attractions such as the temples of Kanchipuram, where they prey on those unfamiliar with local and religious customs. If a priest or guide offers to treat you to a religious ceremony, find out what it will cost you first, and do not allow yourself to be pressured into making "donations" of thousands of rupees — simply walk away if you feel uncomfortable. However, don't get too paranoid: foreigners on the train, or Indian families who want to take your picture on their own camera, for example, are often just genuinely curious.
Same-sex intercourse was decriminalised by a court ruling in 2018. There is a vibrant gay nightlife in metropolitan areas and some (but very few) openly gay celebrities. On the other hand, the law was used as a tool by policemen to harass gays cruising on the streets. You will often see Indian men walking hand-in-hand in the streets, but this is a sign of friendship, not homosexuality.
Whereas Indian men can be really eager to talk to foreigners, women in India often refrain from contact with men. It is an unfortunate fact that if you are a man and you approach a woman in India for even an innocuous purpose like asking for directions, you are putting her on the defensive usually, especially the ones dressed traditionally. It is better to ask a man if one is available (there usually will be), or be extra respectful if you are asking a woman.
Black people may encounter prejudices from the police and the general public about being drug dealers. This reaction stems from the fact that more often than not, foreign-born drug peddlers in India are of Nigerian nationality. Indians find it hard to differentiate between Nigerians and other Africans, others of African descent or even their own Siddi (Indians of sub-Saharan African descent) community, and this behaviour is towards the whole race and not just to any specific country. That said, this behaviour is still considered publicly unacceptable when Indians are confronted by Indians themselves. It is hence wise to keep passports handy at all times, avoid going to areas notorious for illegal activities and maintain contact with respective embassies and, if possible, with other support groups that can vouch for you.
The cow is considered to be a holy animal in Hinduism, and in many Indian states, it is illegal to consume or possess beef or buffalo meat. Non-Hindus suspected of slaughtering cattle or eating beef are also known to have been lynched by fundamentalist Hindu mobs. Prominent exceptions to this taboo are the state of Kerala and the north-eastern parts of the country, where the meat of water buffaloes is widely consumed. Beef continues to be rare.
Driving
As a former British colony, India drives on the left side of the road.
Driving in India can be dangerous. Irresponsible driving habits, insufficient highway infrastructure development, wandering livestock and other hazards make travelling on the country's roads a sometimes nerve-wracking undertaking.
More than 150,000 people died on Indian roads in 2019, the highest figure in the entire world, and that's despite having only 44 cars per 1,000 people (vs. 816 in the United States). The first encounter with a typical Indian highway will no doubt feature a traffic mix of lumbering trucks, speeding maniacs, blithely wandering cows and suicidal pedestrians, all weaving across a narrow, potholed strip of tarmac. To minimise your risk of becoming a grim statistic, use trains instead of buses, use government bus services instead of private ones (which are more likely to force their drivers into inhuman shifts), use taxis instead of auto-rickshaws, avoid travelling at night, and don't hesitate to change taxis or cars if you feel your driver is unsafe.
Of significant concern is that much of the road network is significantly underdeveloped. Most roads are very poorly built and they are full of rubble, large cracks and potholes. Most road signs are not very reliable in the country, and in most cases provide drivers with confusing or inaccurate information. If you are in doubt, ask the locals, normally they are very helpful and willingly provide people with appropriate guidance to a location. Of course the quality of information and willingness to provide it varies, especially in the larger cities.
Female travellers

India is a socially conservative country, and although some Western habits can be perceived as dishonourable for a woman in much of the country, India is coming out of its conservative image rather quickly, especially in big cities. By "conservative", this doesn't mean women are always suppressed because the world's only women run market, the Ima Market (Manipuri: Ima Keithel) in Imphal, Manipur, is a sign of women empowerment. People usually say "Asia's largest women market" but this 500 years old market is the "World's only women run market" and a matter of pride for the whole nation to the world.
- White and/or East Asian females may receive some extra attention (usually in the form of stares) from the locals (particularly men) and in some cases, they may even want to take photographs with you. To a large extent, it's likely that the person who wants to take a photo with you or is staring at you has little to no contact with foreigners. This said, it's still possible to encounter someone who may harass you. Don't be afraid to create a scene and don't feel the need to be polite; no Indian woman (or any woman for that matter) would put up with rotten behaviour like that.
- Being overly friendly and appreciative to Indian men is often seen as a sign of romantic interest. If a man and a woman are seen together or talk to each other quite often, locals may assume that there's something going on between the man and the woman. Make it clear that you are friends or acquaintances; that will usually ward people off.
- Outside of the larger cities, it is unusual for people of the opposite sex to touch each other in public. Even couples (married or otherwise) refrain from public displays of affection. Therefore, it is advised that you do not shake hands with a person of the opposite sex unless the other person extends his/her hand first. The greeting by a Hindu is to bring their palms together in front of their chest, or simply saying namaste or namaskar. Both forms are equally polite and correct, if a little formal. Almost all the people (even if they don't know English) do understand a "hi" or a "Hello". In most parts of northern India and cities, it is quite acceptable to offer a "hello" or "good day" followed by a handshake, regardless of gender.
- Outside of trendy places or high society, women generally do not smoke. In some rural or tribal areas women do smoke, but discreetly.
- Places such as discos and dance clubs are less conservative areas. It is good to leave your things at a hotel and head down there for a drink and some light conversation. Only carry as much change as you think you would require since losing your wallet or passport means that you will waste a considerable time trying to get help.
- People are generally modestly clothed even at the beaches, so be sure to find out what the appropriate attire is for the beach you are visiting. In tourist-oriented places like Goa, where beachgoers are predominantly foreigners, it is permissible to wear bikinis on the beach, but it is still offensive to walk around in them elsewhere. There are a few beaches where women (mostly foreigners) sunbathe topless, but make sure that it is safe and accepted before you do so.
- It's not so safe to walk in isolated places if you are a solo female. Especially at night, avoid walking on streets or lanes without many people and be cautious when taking a taxi or auto-rickshaw at night. Avoid clothes such as tight shorts, a miniskirt, sports bra, tank-top or other clothes which expose a lot of skin, as it can attract unwanted attention. There have been some rapes of foreign women and highly publicised rapes of Indian women, some of whom have been murdered. India has been characterised as one of the "countries with the lowest per capita rates of rape" but a large number of rapes go unreported. The willingness to report rape has increased after several incidents received widespread media attention and triggered widespread public protest. The Indian government of India has also reformed its penal code in relation to crimes of rape and sexual assault.
- In local and suburban trains, there are usually cars reserved only for women and designated as such on their front. In Delhi Metro trains, it is the first compartment.
- In most buses (private and public) a few seats at the front or at one side of the bus are reserved for women. Usually, these seats will be occupied by men and, very often, they vacate the place when a female stands near gesturing her intention to sit there. In many parts of the country, women will not share a seat with a man other than her spouse. If you sit near a man, he may stand up from the seat and give his seat also to you; this is a sign of respect, not rudeness.
- Street parties for holidays are usually filled with crowds of inebriated men. During festivals such as Holi, New Year's Eve, and even Christmas Eve, women can be subjected to groping and sexually aggressive behaviour from a certain section hiding in these crowds. In such an event, just scream or make a scene pointing your finger at the person. People will come to your help. It may be less advisable for women to attend these festivities alone.
- So-called Eve teasing is a common term used in Indian English to refer to anything from unwanted verbal advances to physical sexual assault. Anything overt should be treated in a firm manner and if needed, ask the local populace (women in particular) to try and get the message across. Avoid confrontation if at all possible. Sticking to such an area is not recommended. It's not disrespectful for a woman to tell a man eager to talk to her that she doesn't want to talk: so if a man's behaviour makes you uncomfortable, say so firmly. If he doesn't seem to get the hint, quietly excusing yourself is a better answer than confrontation.
- Befriending Indian women can be a wonderful experience for female visitors, although you might have to initiate conversation. An easy topic to get things going is to talk about clothes, food.
- Dressing in traditional Indian clothes, such as salwaar kameez (comfortable) or saree (more formal and difficult to wear) will often garner Western women more respect in the eyes of locals. The idea is to portray yourself as a normal person, instead of a distanced tourist. Easy clothing is to wear a kurta paired up with jeans or a salwar. They are very comfortable and most of the women do the same.
- Body searches (such as at the airport) by officers of the opposite sex is not allowed in India.

Police and other emergency services
- Like other federal countries, law enforcement is dealt by various agencies in India:
- General policing is responsible for the states and union territories, under various state and union territory police forces.
- Large cities like Mumbai or Bangalore may also have their own police departments, often operating independently from state police forces.
- The Central government also maintain federal law-enforcement agencies responsible for specific duties, such as railway policing, transport security and border patrol.
- Unfortunately, corruption and inefficiency are present in all Indian police forces, and the quality of the police force varies by officer. For emergencies, throughout most of India, you can dial 100 for police assistance. Try to speak the words slowly so that the police officer on phone does not have a problem in comprehending your foreign English accent. For non-emergency crimes, go down to the police station to report them, and insist on getting a receipt of your complaint.
- You should insist the police to make a first information report (FIR) and receive a copy of it if you are reporting any serious crimes, as it is a legal requirement for them to do so. The police will only start the investigation after the FIR is made.
- The emergency contact numbers for most of India are: 100 (Police), 101 (Fire and rescue), and 102 (Emergency medical service). Dialling to neighbouring major hospitals may also work in case of medical emergencies. In Chennai, Hyderabad, Ahmedabad, Bangalore, Kochi and several other cities throughout India, you can dial 108 for all emergencies.
Terrorism
The India-Pakistan conflict, simmering for decades, has manifested in terrorist attacks on India's main cities: since 2007, there have been bombings in Delhi, Mumbai and other big cities. The targets have varied widely, but attacks have usually been aimed at locals rather than visitors. The exception was in 2008, when a shooting spree targeted and killed many foreigners along with Indians, in Mumbai's posh hotels and railway station, etc. All the terrorists involved in this were from Pakistan, and were killed in action except one who was captured alive and later hanged. There is little you can do, however, to avoid such random attacks, but do keep an eye on the national news and on any travel advisories from your embassy.
Stay healthy
|
Avoiding Delhi belly Four quick tips for keeping your stomach happy:
|
Going to India, you have to adapt to a new climate and new food. However, with precautions the chance and severity of any illness can be minimised. Don't stress yourself too much at the beginning of your journey to allow your body to acclimatise to the country. For example, take a day of rest upon arrival, at least on your first visit. Many travellers get ill for wanting to do too much in too little time. Be careful with spicy food if it is not your daily diet.
Tap water is normally not safe for drinking. However, some establishments have water filters/purifiers installed, in which case the water should be safe to drink from them. Packed drinking water (popularly called "mineral water" throughout India) is a better choice. Bisleri, Kinley, Aquafina, Health Plus are popular and safe brands. But if the seal has been tampered, or if the bottle seems crushed, it could be tap water being illegally sold. So always make sure that seal is intact before buying. In Indian Railway stations, a low-priced mineral water brand of Indian Railways is generally available, known as "Rail Neer".
Fruits that can be peeled such as apples and bananas, as well as packaged snacks are always a safe option. Wash any fruit with uncontaminated water before eating it.

No vaccinations are required for entry to India, except for yellow fever if you are coming from an infected area such as Africa. However, Hepatitis (both A and B, depending on your individual circumstances), meningitis and typhoid shots are recommended, as is a booster shot for tetanus.
Diarrhoea is common, and can have many different causes. Bring a standard first-aid kit, plus extra over-the-counter medicine for diarrhea and stomach upset. A re-hydration kit can also be helpful. In case you run out and cannot get the re-hydration solution widely available at pharmacies, remember the salt/sugar/water ratio for oral re-hydration: 1 tsp salt, 8 tsp sugar, for 1 litre of water. Indians have resistance to native bacteria and parasites that visitors do not have. If you have serious diarrhea for more than a day or two, it is best to visit a private hospital. Parasites such as Giardia are a common cause of diarrhea, and may not get better without treatment.
Malaria is endemic throughout India. CDC states that risk exists in all areas, including the cities of Delhi and Mumbai, and at altitudes of less than 2000 metres in Himachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir and Sikkim; however, the risk of infection is considered low in Delhi and the Plains. Get expert advice on malaria preventatives, and take adequate precautions to prevent mosquito bites. Use a mosquito repellent when going outside (particularly during the evenings) and also when sleeping in trains and hotels without air conditioning. A local mosquito repellent used by Indians is Odomos and is available over-the-counter at most medical stores.
If you have asthma, carry enough supplies as dust, pollen or pollution may cause some trouble to your breathing.
It is very important to stay away from the many stray dogs and cats in India, as India has the highest rate of rabies in the world. If you are bitten it is extremely urgent to get to a hospital in a major urban area capable of dealing with rabies. You can get treatment at any major hospital. It is very important to get the rabies vaccine after any contact with animals that includes contact with saliva or blood. Rabies vaccines only work if the full course is given prior to symptoms. The disease is almost invariably fatal otherwise.
If you venture to forests in India, you may encounter venomous snakes. If bitten, try to note the markings of the snake so that the snake can be identified and the correct antidote given. In any event, immediately seek medical care.
Healthcare
Medical care in India is generally of good quality. Virtually all Indian doctors speak English fluently and are highly qualified at their jobs.
Public hospitals tend to be unsanitary, overcrowded, understaffed and underequipped. Private hospitals, on the other hand, are usually of an excellent standard and among the best in the world, making India a popular destination for medical tourism. The downside is that they are usually much more expensive than public hospitals, though still reasonably priced by Western standards. Many private hospitals accept international health insurance; check with the hospital before you go.
One may also consider availing the services of a private clinic. Private medical practices are common throughout the country, and are readily more accessible than hospitals.
There are a few travel clinics in India, that can be checked out by visiting the ISTM website in the larger cities. Most CDC recommended vaccinations are available in many of these travel health clinics in larger cities. Large corporate hospital chains like Fortis, Max, Apollo and similar places are your best bet for emergency medical care in larger cities, and they have better hygiene and generally well trained doctors, some from UK & US institutions.
Respect
|
Kissing in India India can trace kissing back thousands of years in its literature. Indeed, the well-known Kama Sutra has an entire chapter devoted to kissing. However, in most cultures of the Subcontinent, kissing has traditionally been people have been surprised to get into serious trouble for kissing in public, regardless of the nature of their relationship or marriage or their nationality. Opposition to public kissing is not a universal opinion in India; many Indians find kissing acceptable, but because of those who don't, it is best to avoid kissing (even on cheeks) in public while you are there. None of this applies to parents and children kissing each other, though; that's universally acceptable in India. |
Etiquette

- Indians, by and large, are neutral communicators. Although Indians try to be respectful and courteous in social situations, words are often taken at face value. It's important to be explicitly clear and upfront about what you intend to say as euphemisms, idiomatic language, and the like may be misunderstood.
- Direct personal questions (based on your personal life, salary, education, and lifestyle) are commonly asked. To Indians, it's not considered impolite, but rather it's a way to get to know someone fully. In some cases, you may find others giving you advice on whatever it is you're doing, either warranted or unwarranted. Don't feel annoyed or irritated by this as Indians don't intend to patronise or pull you down in any way. If you feel the question was too personal, simply give an indirect answer and move along.
- English is an official language of India. To most Indians, it is a second language, and among a few, it is the first language. Making condescending statements such as "You speak very good English" can be met with offence.
- Indians respect their elders and it would be seen as rude to directly challenge a statement said by someone older than you. You should always try to address people you don't know as 'ma'am' or 'sir', especially if they're older than you, and always act in a mature, sensible fashion around them.
- Family values are highly revered by many Indians. Passing unwarranted comments about someone's family life won't win you friends or praise.
- Indian women generally dress conservatively, although in metropolitan cities more liberal attire can be seen. Women may attract unwanted attention from men depending on how they're dressed.
- It is better to avoid going out on the roads alone, especially in remote places or lanes and by-lanes without many people at night. Keeping some company is always advisable.
- Indians will consider themselves obliged to go out of the way to fulfill a guest's request and will insist very strongly that it is no inconvenience to do so, even if it is not true. This of course means that there is a reciprocal obligation on you as a guest to take extra care not to be a burden.
- Most Indians are not aware that the term "Negro" is considered offensive in some other parts of the world, and they may use it with no intent to offend.
- Note dietary restrictions when inviting Indian friends for a meal. Pork is forbidden to Muslims, while beef is forbidden to followers of most of India's other religions (e.g. Hinduism), though in some states, like Kerala, beef is consumed liberally by Christians and Muslims. Also over 30% of Indians are vegetarian. it is better to ask people what they don't eat beforehand.
- It is customary to put up a token friendly argument with your host or any other member of the group when paying bills at restaurant or while making purchases. The etiquette for this is somewhat complicated.
- In a business lunch or dinner, it is usually clear upfront who is supposed to pay, and there is no need to fight. But if you are someone's personal guest and they take you out to a restaurant, you should offer to pay anyway, and you should insist a lot. Sometimes these fights get a little funny, with each side trying to snatch the bill away from the other, all the time laughing politely. If you don't have experience in these things, chances are, you will lose the chance the first time, but in that case, make sure that you pay the next time. (and try to make sure that there is a next time.) Unless the bill amount is very large do not offer to share it, and only as a second resort after they have refused to let you pay it all.
- The same rule applies when you are making a purchase. If you are purchasing something for yourself, your hosts might still offer to pay for it if the amount is not very high, and sometimes, even if it is. In this situation, unless the amount is very low, you should never lose the fight. (If the amount is ridiculously low, say less than ₹10, then don't insult your hosts by putting up a fight.) Even if by chance you lose the fight to pay the shopkeeper, it is customary to practically thrust (in a nice way, of course) the money into your host's hands.
- These rules do not apply if the host has made it clear beforehand that it is his or her treat, especially for some specific occasion.
|
Naming conventions
|
Religious etiquette
As India has great diversity, people follow different religions. Hinduism is followed by a majority of the people.
General rules
- When visiting temples and mosques, it is obligatory to take off your shoes. The same custom applies to visiting someone's home.
- Christians are a minority in India, but going to church and following your faith are always appreciated. There are different denominations and they differ a bit in their practices.
- It is disrespectful to touch people with your feet. If done accidentally, you will find that Indians will make a quick gesture of apology that involves touching the offended person with the right hand, and then moving the hand to the chest and to the eyes. It is a good idea to emulate that.
- The head is considered to be the holiest part of the body, so avoid touching people on the head, including young children, as this is very offensive to Hindus.
- Books and written materials are treated with respect, as they are treated as concrete/physical forms of the Hindu goddess of knowledge, Saraswati. Never touch a book/written material with your feet.
- Anything associated with wealth is treated with respect as it is treated as concrete/physical forms of Hindu goddess of wealth, Lakshmi.
- The swastika is a common symbol in India. It is also fairly common for Indian parents to name their daughters "Swastika". There is no connection of this symbol to the Nazis. Jewish people have lived in India for thousands of years and have never faced any antisemitism. Drawing parallels between the Swastika and Nazism will not be appreciated.
Things to avoid
Politics:
- Indians, in general, are ardently political, and politics is a very popular conversational subject amongst many Indians, including the older generation. Many Indians have a breadth of political opinions, including that of their own country. As a visitor, you'll be exposed to a breadth of political opinions both publicly and privately, even though most Indians often express frustration with the government. This said though, you could immediately be seen as uninformed if you do not follow Indian news closely. Don't hesitate to engage in political discussions, but it's worth mentioning that being a visitor puts you in a delicate position.
- Do not mention or have a discussion about the Kashmir conflict. It's a highly emotional subject that can very quickly elicit strong reactions from Indian people. On a side note, the whole of Kashmir, including Azad Kashmir and Gilgit Baltistan (the two regions of Kashmir under Pakistani control), legally belongs to India according to the Jammu and Kashmir Instrument of Accession, which was signed during the first Indo-Pak war in the 1940s. Pakistan is the only country that objects to the document. Given the very sensitive nature of the conflict, many Indians express feelings of antipathy towards Pakistan.
- Do not mention or have a discussion about Pakistan. You're unlikely to cause offence by having a discussion about the relationship between India and Pakistan, but attempting to compliment or say anything that could be perceived as positive about Pakistan can evoke a strong response from some Indians. Referring to someone as a "Pakistani" is often used as an insult in India.
- Do not mention or have a discussion about China. The two countries have a tense and complicated relationship, mostly over territorial disputes on their Himalayan border. Some Chinese products are illegal to possess in India and the mere sight of Chinese products can evoke a strong response among some Indians.
- The Partition of India is a sensitive issue. Whilst a few may convey bitterness against the British Empire, the vast majority of people do not have anything against people from the United Kingdom, save those who lived through the horrors of the partition. The two countries enjoy a positive relationship, and it is not uncommon to find people who have relatives or friends living in the UK.
Religion:
- Be extremely careful when discussing religion. Many Indians have liberal, open-minded attitudes towards religion, although there are some who have rigid, radical viewpoints, and fundamentalist Hinduism has seen growing support the 21st century. It's not considered impolite to discuss your religious convictions with someone; for the most part, many Indians are open about talking about it. This said, do not impose your religious beliefs upon someone. Anything hinting at proselytisation is frowned upon in general and will not be appreciated.
- Contrary to popular belief, India is not a vegetarian nation. Vegatarians are a minority in India, comprising 20-30% of the population. Jains, a staunchly vegetarian religious group, are 2-5% of the population. That said, some ardently religious groups and people often try to demonise non-vegetarianism. Many of the more well-aware Indians feel it is a part of a concerted attempt to codify a monolithic idea of Indian culture and are quite embarrassed by this all. These sentiments are more common in North India, but in other places, such as South India and North-East India, people tend to be more liberal and accepting of other beliefs, and don't really mind as much. If visiting someone's house, it's always wise to ask if the person is a vegetarian or a non-vegetarian. Do not impose your meal preferences upon someone; it is frowned upon.
- Atheism is not taboo in India. This said, you should be careful when discussing religion with those who have rigid, radical viewpoints; some atheists in India have been attacked by radical groups for openly criticising religion.
Other things to watch out for
- A lot of Indians tend to have a strong sense of ethnic pride, as many Indian communities around the globe are noted for being well-established. If you have Indian roots, or if you were born and raised overseas, be careful with divulging your opinions on the country and the culture: some may expect you to follow the same norms and nuances like the rest of the populace, and may not take too kindly to your negative feedback.
- Families tend to be close-knit. Tread very carefully if you have Indian roots, if you were born and raised overseas, or if you are in an intimate relationship with an Indian person: You're often expected to align your views with your/their family, and not doing so would result in you being shunned. Bear in mind that this phenomenon is common, so if this ever happens to you, remember that you're not alone.
- Racial relations in India have historically been complex, and you should exercise a degree of respect when discussing that.
- Attitudes towards the LGBT community have been changing since the 2000s. In 2018, homosexuality (which was once punishable by life imprisonment) was decriminalised, and since then there have been strong political movements in favour of LGBT rights. While this may seem impressive, many Indians still have conservative opinions on homosexuality and do not fully understand it. Try not to reveal your sexuality in public as you may invite unwanted comments or stares.
Connect
By phone
The country code for India is +91.
In acronym in India, area codes are called STD codes (Subscriber Trunk Dialing - national long distance) and international dialing is called ISD (International Subscriber Dialing - international long distance).
Local phone numbers can be anywhere from 5-8 digits long. But when the STD code is included, all landline phone numbers in India are 10 digits long. Mobile phone numbers are always 10 digits long and usually start with '9', '8', '7' or '6'. The following table explains how to dial:
| Calling from | Price | Syntax | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Same STD code | Local | number | 12345678 |
| Mobile phone | Local | STD code of the town you are in number | 011-12345678 |
| Mobile phone | STD to mobile phone | number | 012345678 |
| Different STD code | STD | 0-area code-number | 022-12345678 |
| Overseas | ISD | +91-area code-number | +91-22-12345678 |
Toll-free numbers start with 1-800, but are usually operator-dependent: you can't call a BSNL/MTNL toll-free number from an Airtel landline, and vice versa. Often, the numbers may not work from your cellular phone. Other National Numbers that start with 18xx or 19xx may attract special charges.
To dial outside the country from India, prefix the country code with 00, e.g. a US number will be dialed as 00-1-555-555-5555. Calling the Canada/UK/US over the normal telephone line will cost you about ₹7.20 per minute. Calls to other countries, particularly to the Middle East, can be more expensive.
Payphones, called public call offices or PCOs are now increasingly rare with the ubiquitous availability of mobile phones. Where they exist, they are usually staffed, and you dial yourself but pay to the attendant after the call is over. Metering is done per pulse and a service charge of ₹2 is added to the bill. Larger cities also have Western-style unmanned public phones, which are usually red in colour and accept one rupee coins.
Mobile
Airtel, Vodafone Idea, Reliance JIO and BSNL-MTNL are mobile service provider in India. Airtel, Vodafone, and JIO provide services to the whole of India. There is no extra cost for roaming across India. You can use call, data and SMS services everywhere. India to India maximum call rate is ₹1 per minute. You can buy 1GB (2G, 3G or 4G) data for less than ₹20. You can use 4G and 4G VoLTE services everywhere. The Jio and Airtel 4G (LTE and VoLTE) networks cover 95% of the population of India. You can buy a keypad mobile for ₹500. Touch mobiles retail from ₹4,000.
You need a validity recharge to use your data, calls and SMS. If you don't have any validity (or unlimited) plan, you cannot use data, text, or make calls. Airtel and Vodafone Idea (VI) gives one-month validity for ₹49.
Calling overseas can cost quite a bit and will depend on the location you're calling to. In contrast, the other way round (calling to India from elsewhere) is cheap.
Unlimited Recharge
All operators provide unlimited calls in all India. With an unlimited pack, you can talk unlimitedly anywhere in India. Unlimited plans start at ₹129 for 28 days. All operators have almost the same plans for all users.
By internet
Wi-Fi hotspots in India are, for the most part, limited. All airports and railway stations do offer free high speed Wi-Fi. Delhi, Bangalore, Pune and Mumbai are the only cities with decent Wi-Fi coverage. Many free Wi-Fi services will require entering a One time password (OTP) sent to an Indian cell phone number.
As restrictions on internet use increase in India, many vendors refuse to sell SIM cards to foreigners (or anyone without local ID) which was not always the case: you may find an Indian resident or hotel employee willing to buy one under their name if suitably motivated. This might be the best option. To get a SIM card alone as a foreigner, you are suggested to visit the telecom operator's exclusive store.
- Mobile internet is very cheap to obtain, especially with the proliferation of low-cost operator Reliance Jio, which has forced the mainstream operators such as Airtel and Vodafone Idea to follow suit. It is not hard to find reasonable deals (like 1 GB per day for a month) for ₹200 ($3) or so. 4G connectivity is available in most places, with 3G in some remote locations. If you use the train, you may occasionally find pocket regions where the internet drops to 2G or goes away completely.
- Internet cafes are common and they charge as little as ₹10-20 per hour. Many will ask for your passport or ID. Beware of using your credit cards online as there have been many cases of credit cards thefts using keyloggers.
- Public libraries have PCs with broadband for public use. Most libraries require a membership but government-operated libraries only require a quick registration with the verification of your ID.
Internet censorship in India is considered “selective”. There are occasional random, inexplicable and arbitrary attempts by the government to block some sites it considers as carrying hateful propaganda, but enforcement is spotty and the decisions are often forgotten after a few month of being made. The site which are blocked by the courts remain strictly blocked and is different from the vague blocks by the government. You are unlikely to find any useful site blocked.
By mail
Addressing mail with a properly-formatted address will expedite its journey with government owned India Post. The PIN code (postal index number) is important, and you can look up PIN codes and correct address formats on India Post's website. A 6-digit PIN code identifies the post office of a district; a 4-digit Post box number (recommended but optional) may narrow this to one business or an individual building. Addresses should be written in three to four lines with the name of recipient, house number and suite or apartment or building number, street name, city or town, state name, PIN code, e.g.:
United Nations House
55/73 Lodhi Estate
New Delhi, Delhi-110003
First class mails get free air lift within India. International first class mail has a maximum limit of 20kg. Prices vary from country to country. A full list related to the pricing can be found in India Post's website. All locations with a PIN code are considered domestic. Military mail is operated by the Army Postal Service through its APOs and FPOs. Domestic posts can be made at an affordable cost of ₹15 ($0.40) for every 50 grams.
Private international carriers like FedEx, DHL and UPS also operate though all major cities.
Cope
For immediate police assistance you can call the emergency number 112.
The Ministry of Tourism has a 24X7 helpline for tourists in need. You can call the helpline number at 1800-11-1363 or just 1363.
Consular assistance
All major cities have international consular assistance which include high commissions, embassies and consulates. More information can be found in respective city articles. Here are links to consular assistance in some cities:
Newspapers
Local Indian English newspapers can be handy and reliable sources for day-to-day updates about the country. India has number of English newspapers and magazines that are published daily, weekly and bi-weekly. Some of the major ones are Business Standard, Daily News and Analysis, Deccan Herald, The Hindu, The Statesman, The Telegraph, The Times of India, The Tribune and many more. Some popular magazines are Filmfare, Down to Earth, India Today, Forbes India and Vogue.
Radio
- AIR FM Rainbow offers hourly news broadcasts at 102.6MHZ.
- AIR FM Gold offers hourly news broadcasts at 100.1MHZ
- Radio One offers modern and retro song broadcasts at 94.3MHZ.
- Red FM offers public talks and entertainment at 93.5MHZ